I. Introduction
Semiconductor lighting (light-emitting diodes, LED) is a new high-efficiency solid-state light source with significant advantages such as energy saving, environmental protection and long life, which will lead to the transformation of the world lighting industry and the rise of the emerging semiconductor lighting industry.
Semiconductor lighting is energy-saving "rich mine", the same brightness consumption is only 1/10 of ordinary incandescent lamps, 1/2 of energy-saving lamps, the service life can be extended by 100 times.
With the rapid advancement of LED technology and the emergence of new applications, energy-saving effects have emerged in the field of special lighting. For example, landscape lighting (replacement of neon lights) energy saving 70%, traffic lights (alternative incandescent lamps) energy saving 80%, if you can enter general lighting in 2010, the effect of energy saving will be more significant.
Second, high power LED
1. Explanation of terms
In terms of power consumption, we usually refer to the milliwatt-level LED as low power and the tile-level LED as high power.
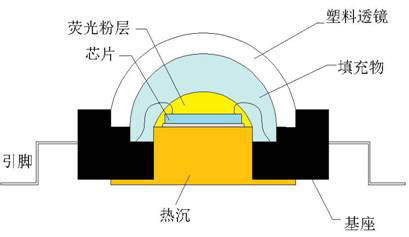
Figure 1 LED package schematic
2. At present, the high-power LEDs commonly seen are divided into two types: single-chip large size and multi-chip small size combination.

Figure 2 High Power LED (top view)
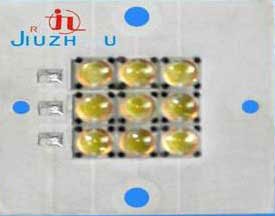
Figure 3 high power LED module
Third, secondary optical design
1. Explanation of terms

![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)