The Corporate Hall of Fame in the RF industry and how they will be affected by the development of 5G;
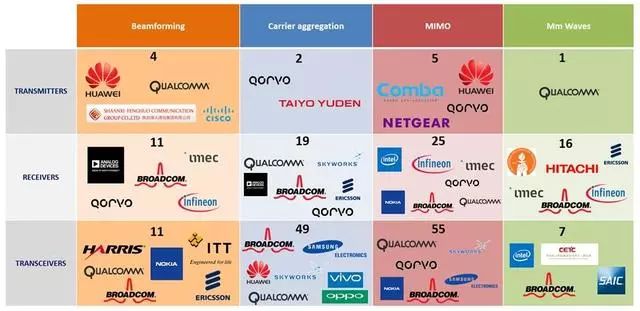
Figure 1. Company Hall of Fame in the RF Industry
Although the mobile industry had previously completed a love-like carnival at the annual Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, ​​high-tech suppliers, system OEMs, and mobile operators are facing problems that have not yet truly addressed the obstacles to 5G development. In fact, these development obstacles have only just begun.
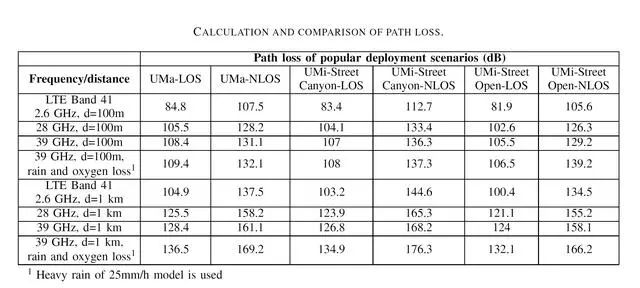
Figure 2. Comparison of propagation loss of high-frequency millimeter-wave and low-frequency waves
The technical problems of 5G development are manifold. Among them, smart antennas and RF front ends for 5G millimeter waves (generally expected to operate at 28 GHz, 39 GHz or 60 GHz) may seriously affect the performance of 5G mmWave handsets that have not yet emerged.
Figure 3, 5G ecosystem
After returning from the Mobile World Congress, Claire Troadec, head of radio frequency (RF) electronics business at the market research company (Yole Développement), told us: "Although many companies such as Qualcomm, Intel, MediaTek and Samsung are using cell phone prototypes as 5G mmWave (millimeter wave Demo platform, but we do not believe that the current mobile phone will be the preferred application terminal form of 5G mmWave. In contrast, 5G millimeter wave will be more likely to be the choice of a fixed data modem on the desktop or desktop so that Consumers can download or transfer large-scale streaming broadband applications."

Figure 4. Qualcomm's 5G millimeter wave prototype
why is it like this?
In view of the high propagation loss of 5G mmWave (millimeter wave) frequency band, the directionality and the sensitivity to blocking are notorious for the engineers in the industry, and it is difficult to design a 5G mobile phone that is always working without losing the signal. Easy things. Consumers may be forced to stay on a page literally or on a picture, and the system will need to look for signals in other frequency bands.

Figure 5 and 5G are applied in the Korean Olympic Winter Games
Another challenge in deploying 5G millimeter-wave radios in mobile handsets is battery life and power consumption. During the Pyeongchang 2018 Winter Olympics, Samsung believes it has demonstrated its own 5G tablet. Although it works well, it's an alarming reminder at Mobile World Congress that this cool application: The battery is dead after 30 minutes.
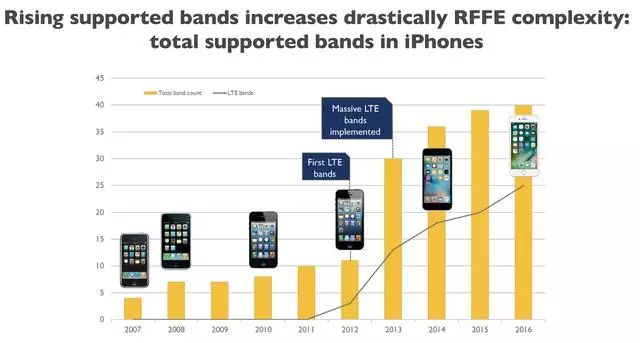
Figure 6. More and more frequency bands need to be supported by smart phones
When asked about this rumors, Yole's Troadec said she thinks there is a problem with high energy consumption during the transmission of mobile 5G mmWave broadcast signals. She suspects that “most manufacturers’ leaders are widely Focus on this area.†But she added that she found that these technology vendors may offer some remedial measures for this apparently problematic system-level power consumption problem in 5G New Radio applications. She said that no one is willing to further discuss this issue at the show, and everyone is consciously avoiding this issue.
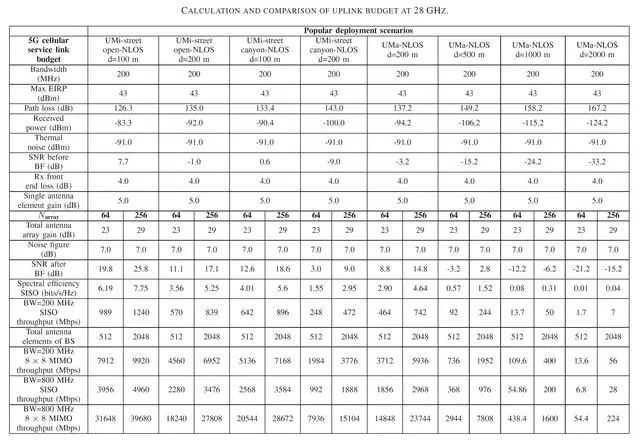
Figure 7, 28GHz uplink budget
The 5G mmWave (millimeter wave) RF (Radio Frequency) module will bring interference to the emerging 5G market not limited to technological changes. The suppliers that are currently in the supply chain that supply 3G and 4G RF components and modules are deeply affected.
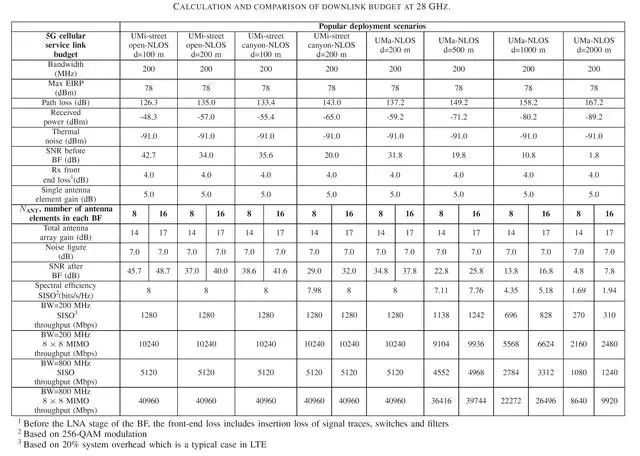
Figure 8, 28GHz downlink budget table
Since 5G mmWave (millimeter wave) may allow suppliers to use CMOS or SOI technology to design RF front-end modules in SoCs, the field will open to the RF market for "advanced CMOS designers and manufacturers" currently facing the handset ecosystem architecture. door. In addition to Intel and Qualcomm, candidates with a presence in this area include Samsung, Huawei, and MediaTek.
More frequency bands, more RF front ends (RFFE, RF front ends)
The mobile industry has come a long way as technology vendors battle with RF Front End (RFFE) modules that can handle an ever-increasing number of frequency bands. According to Teleec, as the cellular standard evolved from 3G to 4G, the number of bands that the RF front-end must deal with increased from 4 to 30.
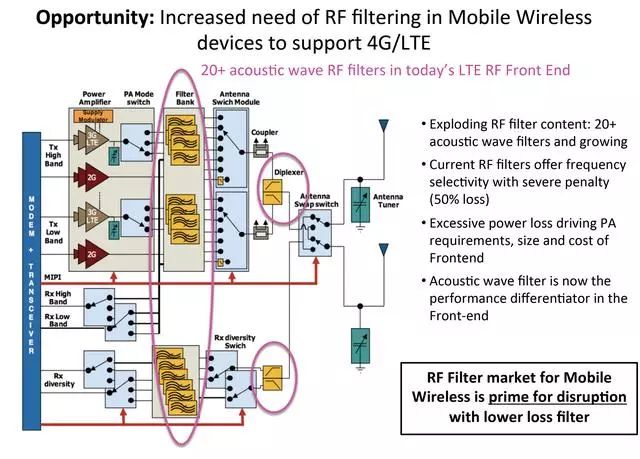
Figure 9. The design of the terminal RF front-end is becoming more and more complex
The increase in the number of bands supported in smart phones will only increase the complexity of the radio front-end.
But with 5G technologies and applications coming online, things will get more complicated. Although theoretically 5G is a single standard, it has three main elements: 5G-supported Internet of Things (IoT) applications, 5G using the sub-6 GHz band, and 5G using mmWave. In terms of radio frequency technology, Teleec observed that "this means that technologies that require very dissimilar performance are grouped together in one device."
Figure 10: Increasing shipments of smart phones
This means that 5G will follow "different stages of implementation, different parallel development of 5G versions." In other words, there will not be a single, unified 5G RF front end (RFFE, RF front ends), but "5G IoT, 5G sub-6 GHz and 5GmmWave (millimeter wave) will follow their own development path , and use their respective RF SiP development to create a parallel ecosystem, "she said.
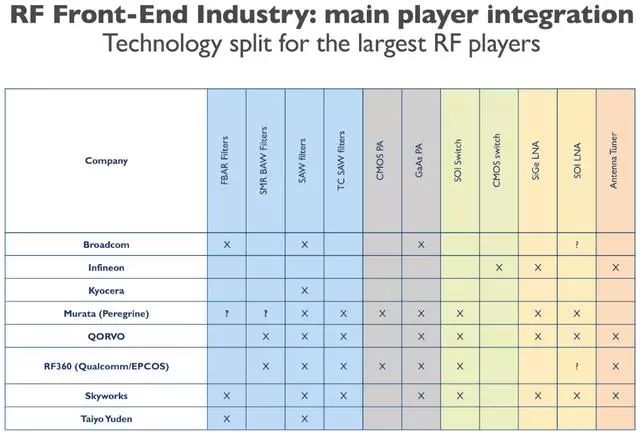
Figure 11. Major players in the RF front-end industry chain
When asked to evaluate the research paths for different RF front ends (RFFEs) of each 5G technology, Troadec said she saw the 5G mmWave technology bring the most disruptive innovation. She expects that 5G mmWave (millimeter wave) needs to change the design and use new materials.
The good news is that 5G mmWave (millimeter wave) can end the practice of the complex front-end modules based on System-in-Package (SiP) technology currently used in 2G, 3G and 4G RF front-end systems. "You can design each building block based on advanced CMOS or SOI technology - including power amplifiers, low noise amplifiers, filters, switches and passives," explains Teleec. This will provide opportunities for many digital chip vendors that previously had little radio expertise to develop SoC front-end modules.
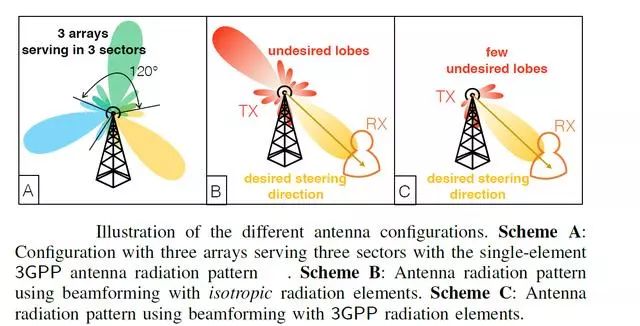
Fig. 12, Beamforming has important application in 5G network
At the same time, for 5G technology in the frequency band below 6 GHz, Tubeec believes it will build on incremental innovation. She explained that in this band, it is expected that the current RF encapsulation architecture changes will only require minimal changes in the bill of materials (BoM, bill of materials).
Since the 5G Internet of Things (IoT) will use frequencies below the 1 GHz band, Tuberec believes that "few or little innovations" are required for semiconductor packages with 5G RF front-ends (RFFE, RF front ends) in this band. . Nonetheless, the 5G Internet of Things (IoT) specifications and protocols designed to address the transmission of data generated by many Internet of Things (IoT) devices have not yet been defined and standardized.
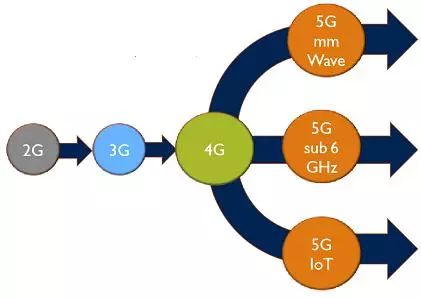
Fig. 13 Different flavors of 5G technologies are being developed in parallel
Today's Hall of Fame in a radio frequency (RF) device or component supply chain
Before delving into the detailed radio frequency (RF) solutions in 5G, let's take a closer look at current RF component and module vendors.
Typically, a radio frequency (RF) front-end module is composed of radio frequency (RF) device components such as RF switches, power amplifiers (PAs)/low noise amplifiers (LNAs), RF filters, and antenna devices (tuners and switches). .
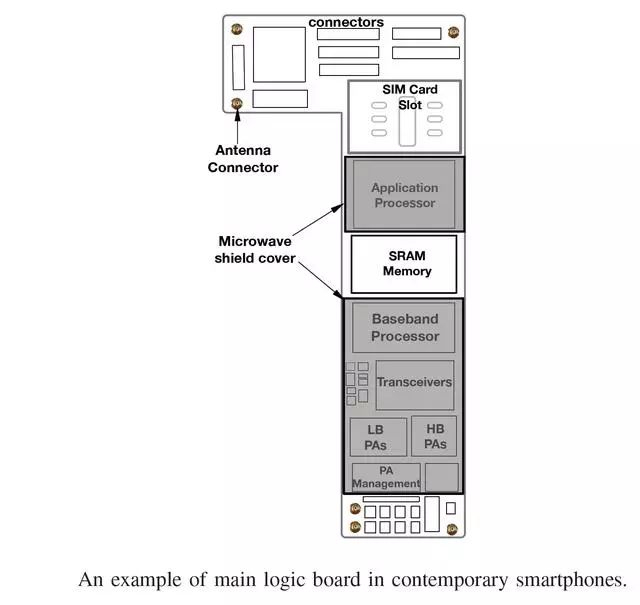
Functional Dividing of Circuits in Figure 14 and 5G User Terminals
Major vendors in the supply chain with RF front-end module congestion include: Sony, Murata (acquired Peregrin Semiconductor in late 2014), Skyworks, Qorvo, Infineon, Broadcom/Avago, Cavendish Kinetics, TDK EPCOS, Qualcomm, Hass et al.
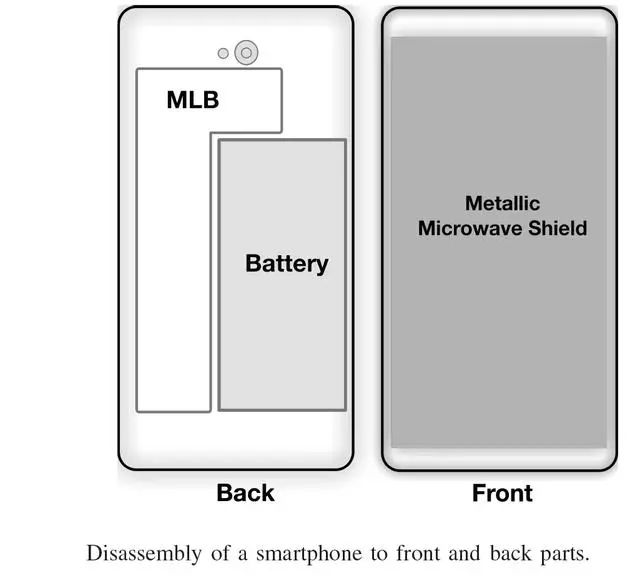
Figure 15: Typical structure of a smart phone
Each company has its own special radio frequency (RF) components that often require the deployment of various substrates and process technologies. Their process technology options range from RF-SOI and BiCMOS to bulk CMOS, GaN and RF MEMS.
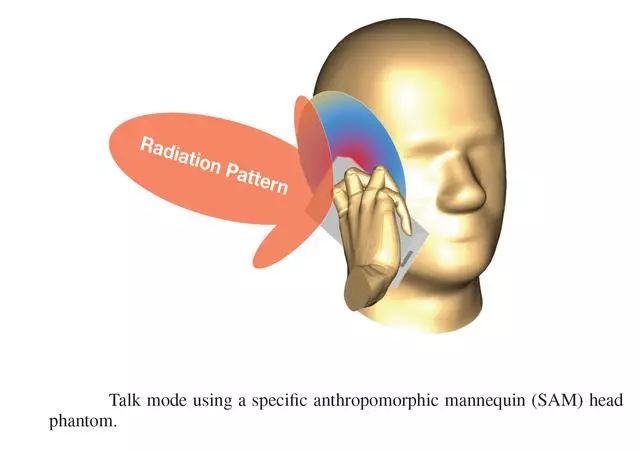
Figure 16: Beamforming for smartphones
Because different types of RF components use a variety of process technologies, the integrated routing path for today's radio frequency (RF) modules is in SiP rather than SoC form.
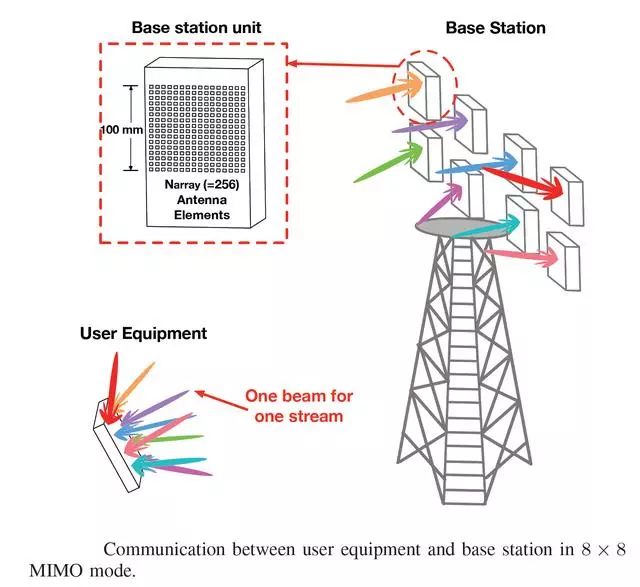
Figure 17 Beamforming technology in 5G network
Today, for 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G frequency bands below 6 GHz (for all frequency bands below 6 GHz), "satisfied with the stringent radio performance requirements in smartphones will be only SiP technology," confirmed Trocare.
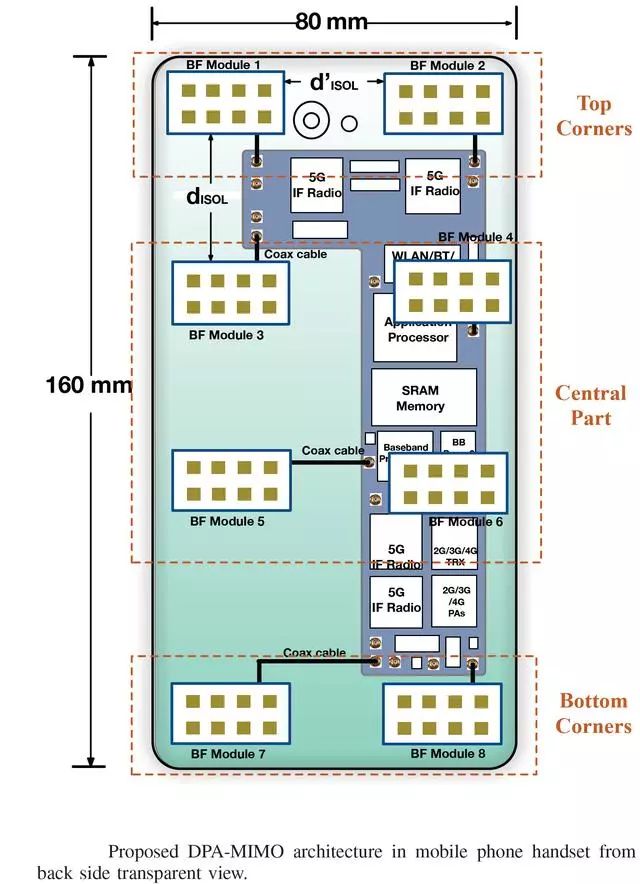
Figure 18. Functional layout in smart phones
There is currently no single RF component supplier that has all the best technology. Troadec explained that in the RF front-end integration, "Each building block requires a very dedicated technology: the best PA using GaAs technology, the best switch using SOI technology, the best filter using SAW and BAW technology and use SiGe technology is the best LNA, etc."
When asked who will provide SiP technology for RF front-end modules, Troadec said: "Broadcom, Murata, Qorvo, Skyworks and TDK / Qualcomm are the only vendors that can provide SiP process technology today."
She explained that each product has its own characteristic requirements, such as high-frequency module, intermediate frequency module, low-frequency module and diversified receiving module, or adopts PAMiD integrated form (highly-integrated custom module, performance-driven but with powerful function and therefore only Limited to Apple, Samsung, Huawei and other players) either adopts the FEMiD integration form (provides a good compromise in performance and cost, and is favored by second-tier smartphone manufacturers such as LG and Chinese mobile gamers).
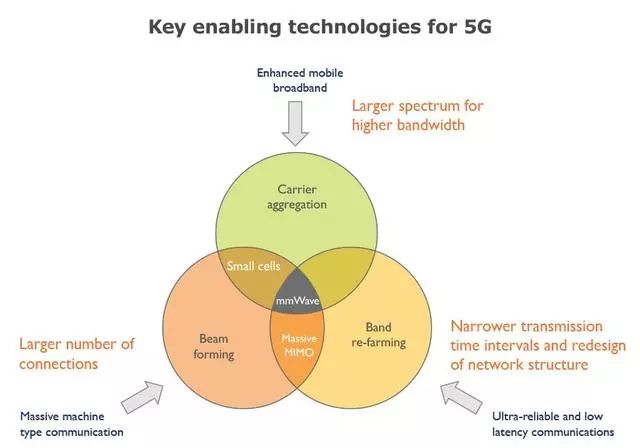
Figure 19, the key technologies involved in the 5G system
“We do see that only a few companies can play a role in this high-tech mixed environment,†she concludes.
5G within a few GHz bands: Still using the SiP method
As the cellular industry develops towards 5G, the same principles (ie adopting the SiP integration method) will continue to exist for GHz 5G RF front-end modules.
Figure 20, Possible Applications of SiP Technology in the 5G Era
However, according to Yole, there will be some changes in terms of more integration of SiP and packaging. Troadec explained that these new measures include the integration of LNAs and switches on the same die based on the SOI platform, and more wafer-level packaging for filters to obtain die size gains (for example, only Broadcom today.) Use this method, and Qorvo is developing this method). In addition, the wafer-level approach will be suitable for packaged power amplifiers (wired connections are still used today) to achieve die size gains.
5G mmWave (millimeter wave): From SiP to SoC
The 5G mmWave RF front end module will undoubtedly revolutionize the most complex RF (radio frequency) component/module supply chain. A large number of complex RF (Radio Frequency) components have been manufactured using different process technologies. On the contrary, the possibility of implementing mmWave front-end modules in SoCs based on advanced CMOS or SOI technology is imminent.
There are many reasons why 5G mmWave (millimeter wave) can design RF (radio frequency) module in SoC.
First, 5G mmWave means moving to the available ultra-wideband spectrum region, Teleec explained. "So we don't need a lot of discrete frequency bands to send information. So the architecture of the RF transceiver can be much simpler."
As a result, this also reduces the restrictions on filter technology, she explained. “We don't need high-end filtering in the module.†However, she warned, “We need advanced switching technologies that switch between different radio technologies (4G or 5G and 5G millimeter waves below 6 GHz) (high isolation) Degree, high linearity. ".
She also pointed out that in 4G, "we use carrier aggregation with a signal bandwidth of 20 MHz per band and use multiple frequency bands. Therefore, we need advanced high-end filter technology (steep suppression curve) to distinguish between Each signal in each band, today only BAW (FBAR) device technology (MEMS technology) can meet this requirement."
Another important factor is that 5G mmWave (millimeter wave) will use beamforming technology, allowing it to shape the beam to simultaneously send information to multiple users. "This will reduce the power amplifier's power emission limitations and requirements. This in turn means that CMOS technology can play a role. "She added:" In the mmWave (millimeter wave) frequency, the inductance becomes smaller; therefore, the passive device Integration with CMOS / SOI technology becomes possible. "
However, Broadec reiterated that for the 5G mmWave (millimeter wave) RF module, a limiting factor seems to be the power consumption of the entire system. "Why do we need to clarify this matter? Because it has a very large impact on the usability of millimeter waves; but so far no one is willing to technically tell us why this is happening and what we need to do." solve this problem.
New players entering the field of RF devices
Once the industry shifts to using CMOS or SOI technology to design 5G mmWave RF front-end modules in SoCs, the current RF front-end device field will be from the seemingly comfortable RF front-end module supplier clubs (such as Broadcom, Murata, Qorvo, Skyworks , as well as TDK / Qualcomm) will change.
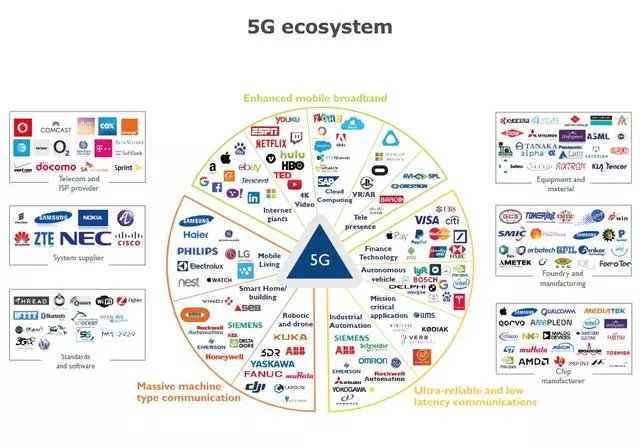
Figure 21, the main players in the 5G ecosystem
Troadec pointed out that Intel and Qualcomm have entered the modem and mobile transceiver business. They are very hopeful to master the wireless RF field to provide end-to-end solutions. The goal of these companies is "the complete internal design of the RF industry chain from A to Z," she said.
If Broadcom acquires Qualcomm...
In the Broadcom (Broadcom) and Qualcomm (Qualcomm) company's various products and technology areas, the mobile phone market is the market for these two giants complementary business. Troadec observed Broadcom in the wireless and Wi-Fi space, while Qualcomm (applications), processor, modems, transceivers, Wi-Fi/BT, plus NXP NFC and their The Microcontroller has a very high status.
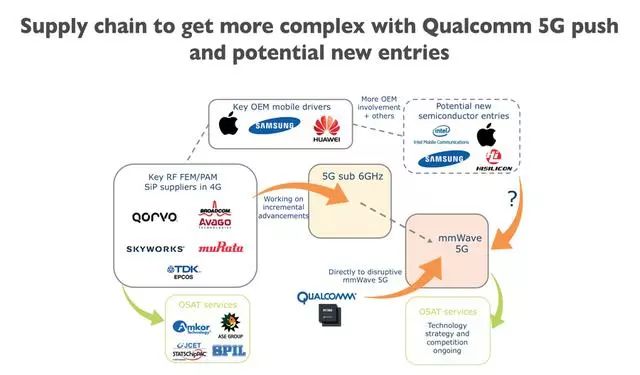
Figure 22: Qualcomm promotes the integration of 5G RF supply chain
Now Qualcomm has acquired strong technical traction in the 5G mmWave (millimeter wave) field, while Qualcomm (Qualcomm) focuses on technical solutions below 6 GHz, said Troadec, if not blocked by the US president, Broadcom The merger with Qualcomm "will create a very high monopoly." She suspects, "That's why we see Intel become scared and try to enter into this acquisition discussion and even put a call to buy Broadcom ( Broadcom)."
Disclaimer: This article is reproduced on the CSDN blog, copyrighted by the original author. The purpose of reprinting is to convey more information and does not mean that this site agrees with its views and is responsible for its authenticity. If it involves works, copyrights and other issues, please contact us to delete!
we are the best supplier in China to offer the networking tools including sort of insertion tools, impact and punch down tool (Ericsson punch down tool, Siemens punch down tool, Corning punch down tool and so on), crimping tool(RJ45 crimping tools, coaxial cable crimping tool, picabond ratchet crimper), cable stripper and cutter, Cable Tester and connector removal tool, and so on.
In short, we offer the networking tools for cutting and stripping coaxial cable, twist cable, and optical fiber. And professional compression crimping tool for different connectors, insertion tools for different modules .To save cost for customers, we have desired some tools with multi-function. So you can keep one tool instead of several different types. Meanwhile, for some coaxial cable crimping tool you can change the head to fit the cable specification yourself. It will make you lose weight on tool set but to finish your work perfectly.

Insertion Tool, Punch Tool, Cat 5 Cable Tester, Crimping Pliers, Cable Crimping Tool
NINGBO YULIANG TELECOM MUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD. , https://www.yltelecom.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)