With the release of iPhone X, 3D face recognition has once become a new technology that people are talking about. At the same time, the release of the domestic Vivo X20 also mentions its face recognition function. Let the professional team of SITRI lead Everyone unveiled the mystery of face recognition.
Let’s start with Apple iPhone X. Let’s take a look at what sensors are in this cute “Qi Liu Hai�
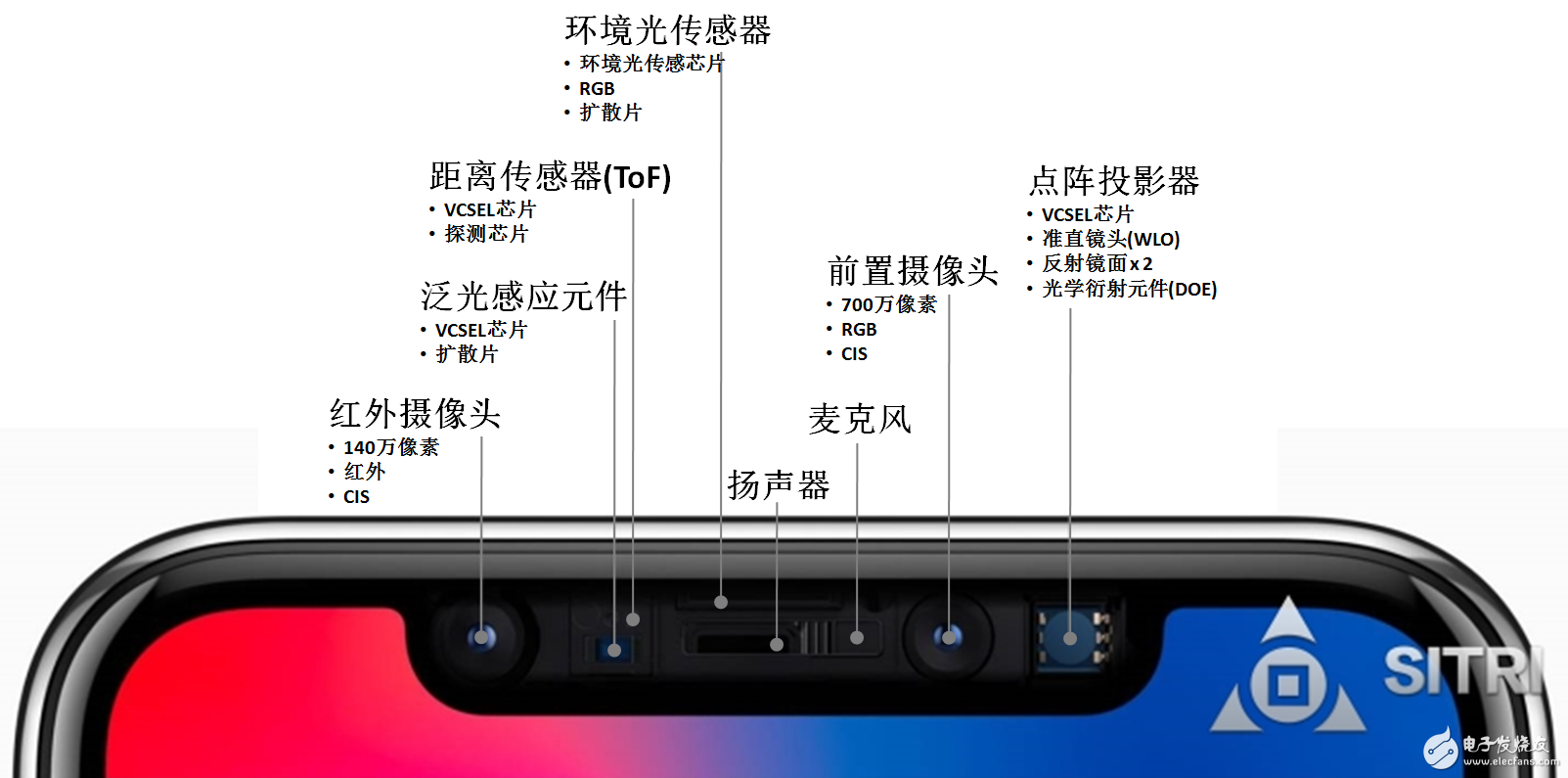
After understanding the sensors in Qi Qihai, are there many new terms? For example, "dot array projectors" and "flooding sensor components", as well as infrared cameras that have never appeared on iPhone smartphone products. These new devices have emerged because the iPhone X introduced a 3D face recognition system.
Before introducing specific sensor information, let's briefly talk about the startup steps of face recognition.
Step 1: When an object approaches the phone, the distance sensor (ToF) will be activated first.
Step 2: The start of the distance sensor (ToF) will activate the flood sensor and the infrared camera. The VCSEL Chip in the flood sensor will emit a number of infrared light. The infrared light is reflected back and captured by the infrared camera to determine whether it is a human face. information.
Step 3: If the face information is judged by the judgment, the dot matrix projector will be activated, and the dot matrix projector will emit about 30,000 infrared structure light spots, and the 3D face information is captured by the infrared camera to perform the image of the face. Information extraction, through the comparison of the A11 biomimetic processor, the face recognition information is obtained.
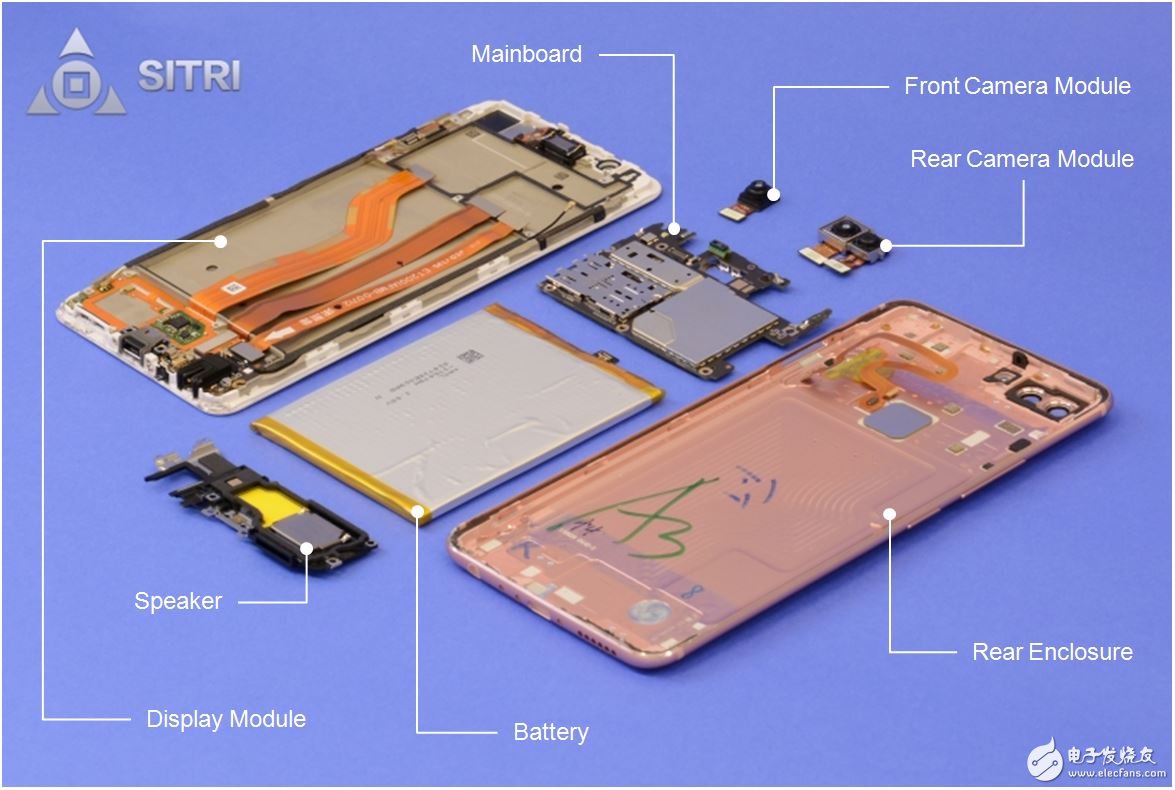
The following is the topic, bringing the iPhone X's 3D face recognition sensor to the secret. Start with the iPhone X's overall structure and main components.
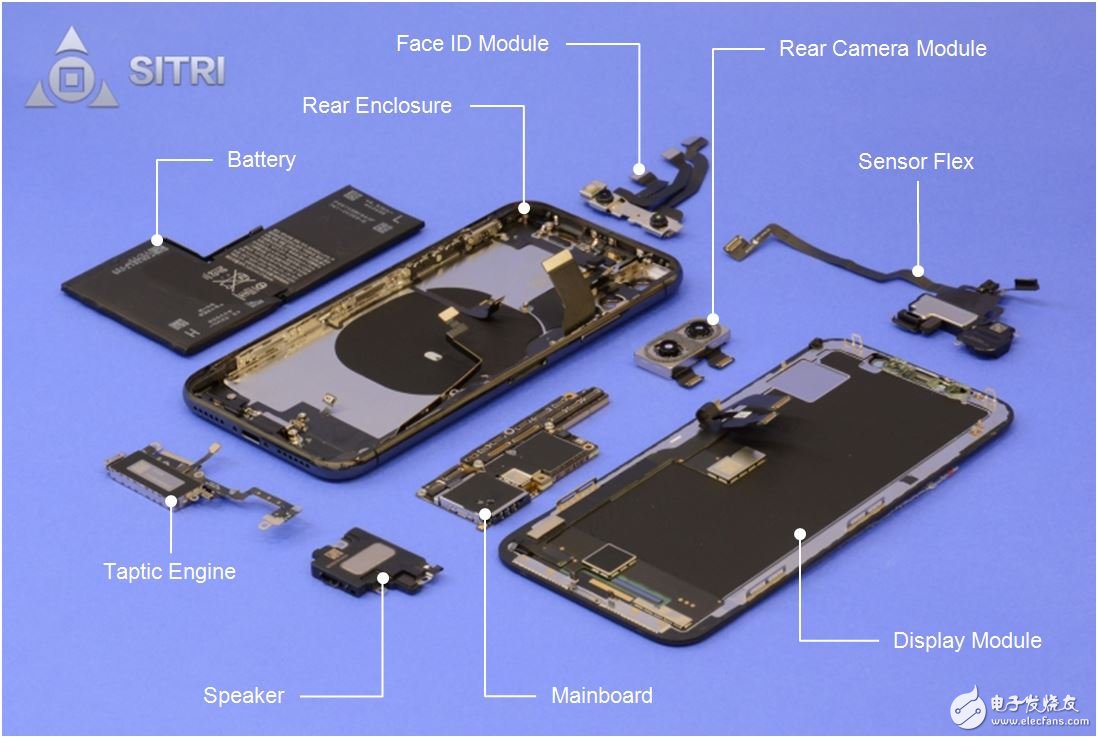
iPhone X machine structure
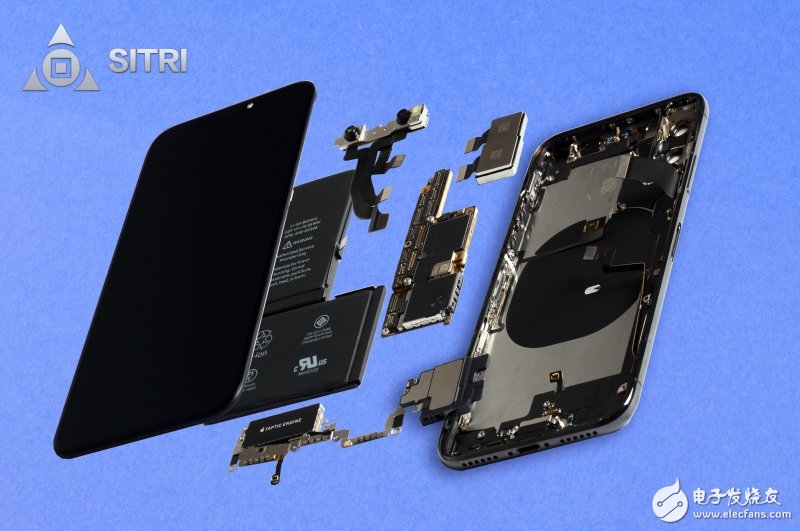

iPhone X main parts diagram
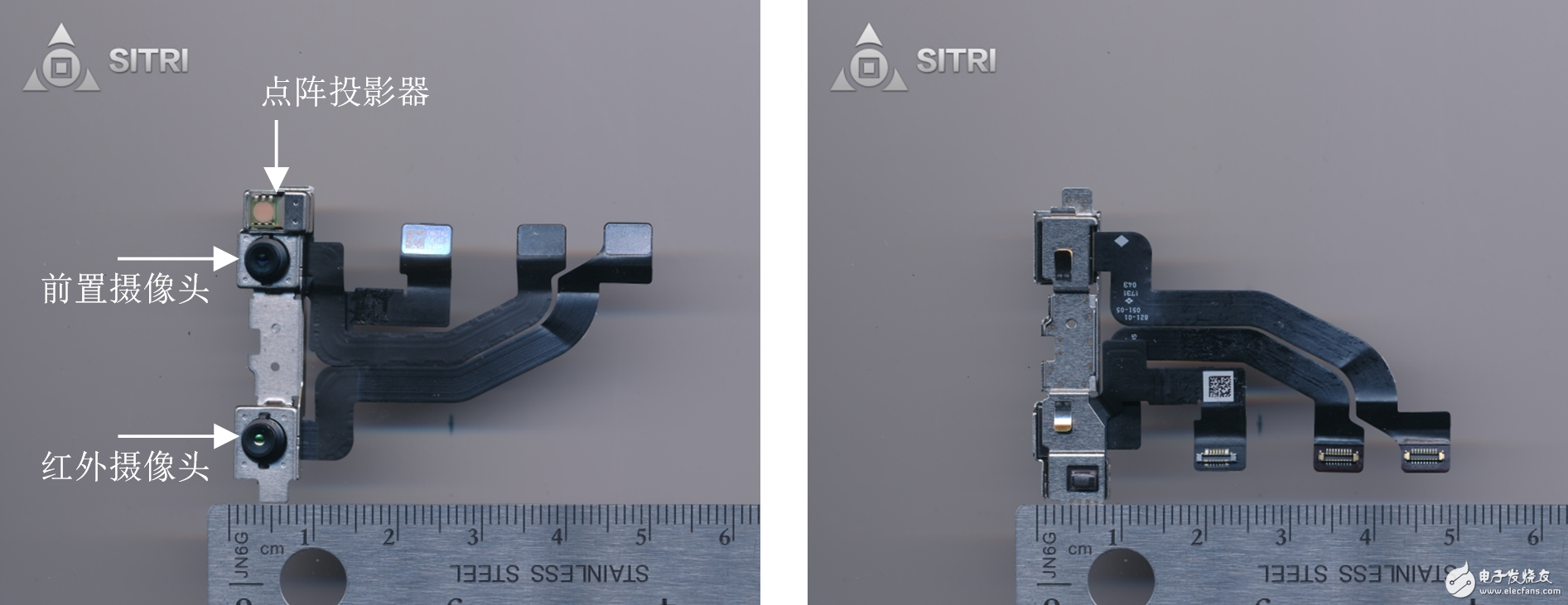
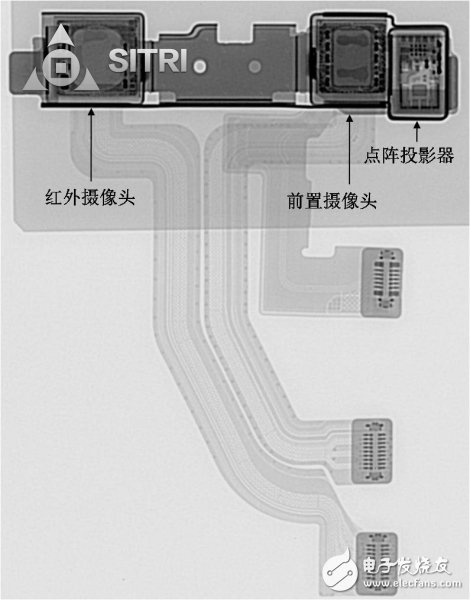
Dot matrix projector
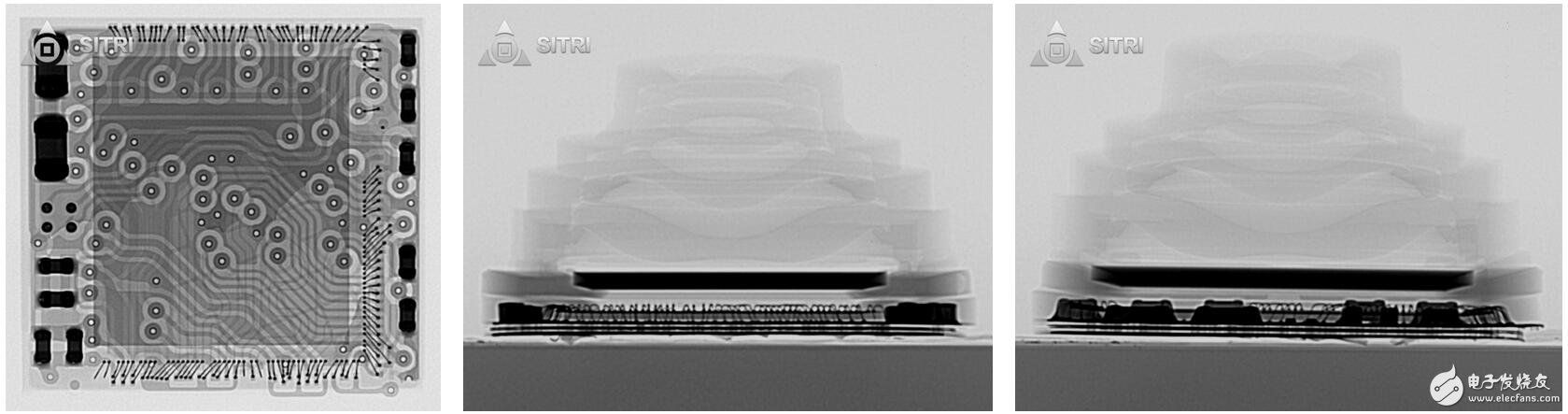
The dot matrix projector and two cameras (infrared camera and front camera) are integrated on one module.
Module scanning

Module X-Ray photo
The dot matrix projector is disassembled to obtain a module of a separate dot matrix projector.
Dot matrix projector module
Dot matrix projector module X-Ray photo
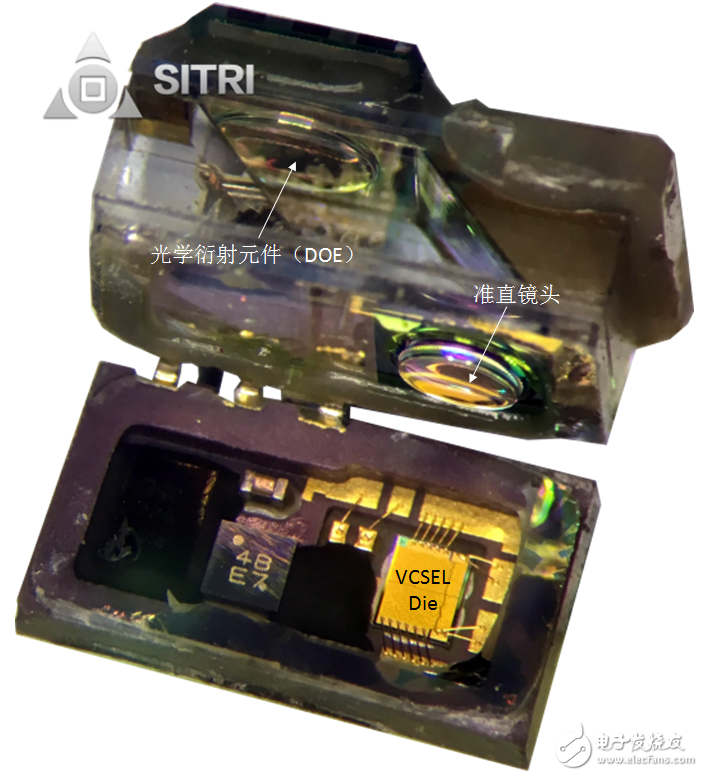
There is a VCSEL chip in the dot matrix projector. When the dot matrix projector is activated, the infrared light emitted by the VCSEL chip is emitted through the collimating lens directly above the chip, passes through two mirror surfaces, and finally passes through the optical diffraction element (DOE). ) Forming about 30,000 infrared structures to emit light.
Dot matrix projector (before opening)

Dot matrix projector (after opening the cover)

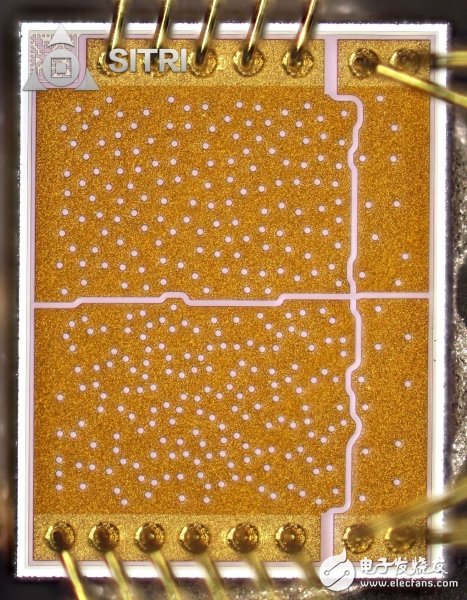
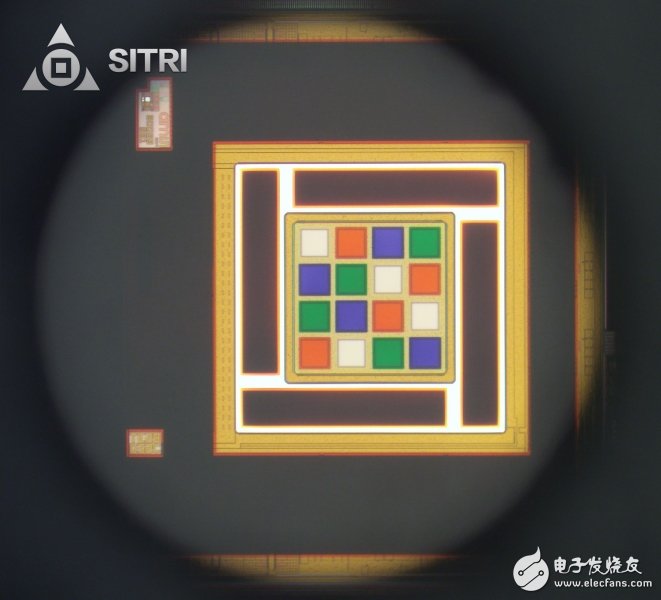
After the above collimating lens and optical diffraction element module are removed, the following VCSEL chip can be clearly seen.
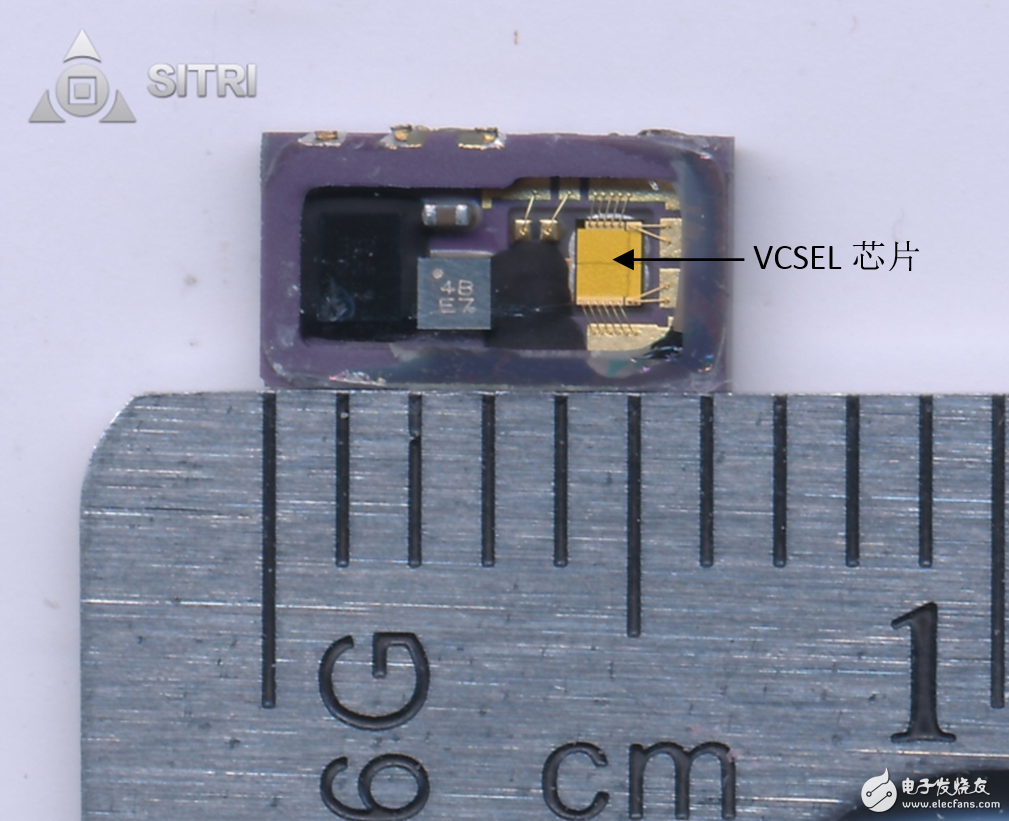
VCSEL chip optical microscope

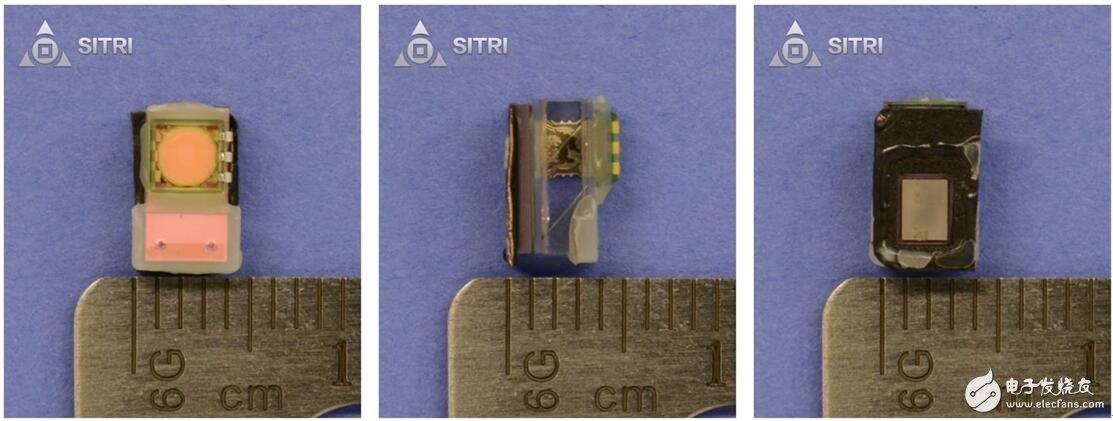
Flood light sensing element
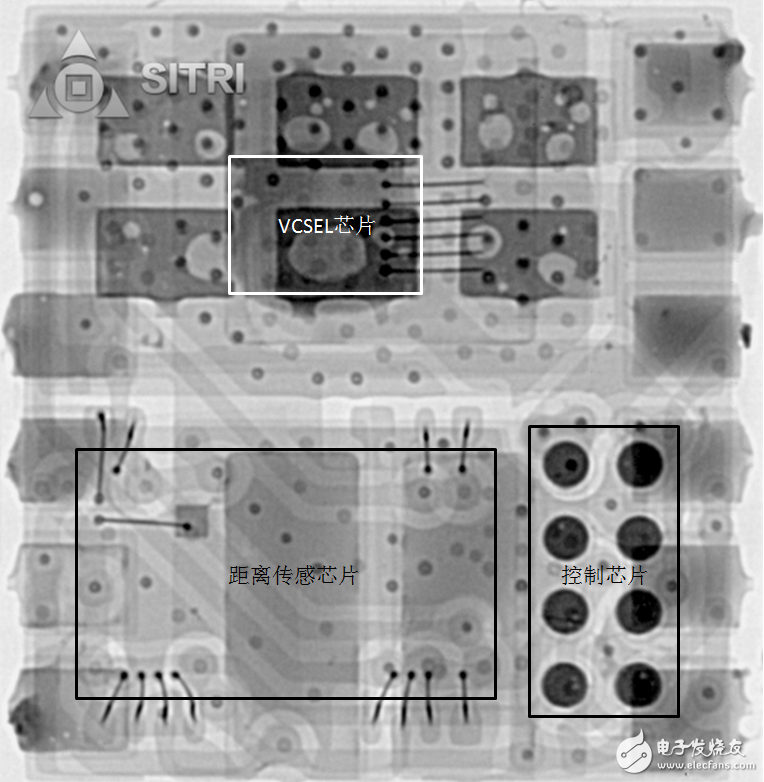
The floodlight sensing element, the distance sensor and a control chip are packaged together. The figure below shows the microscope image of the entire package.
Whole module optical microscope
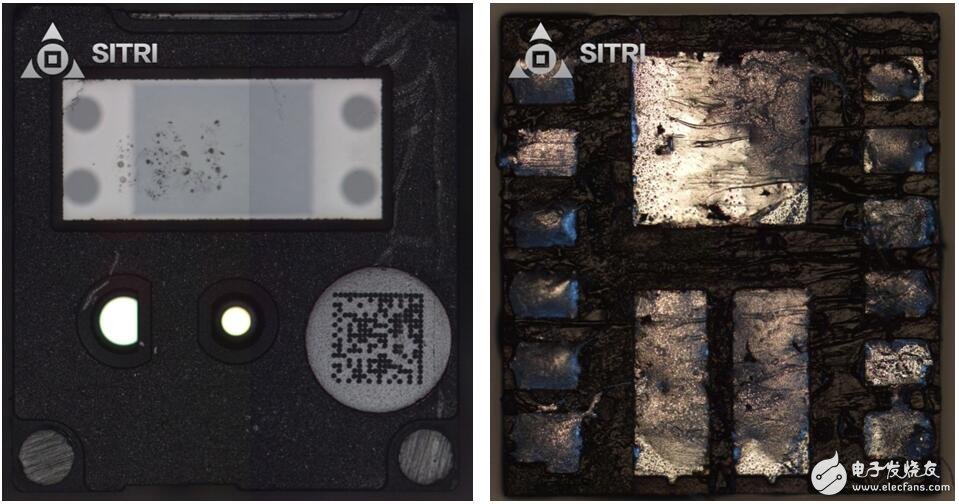

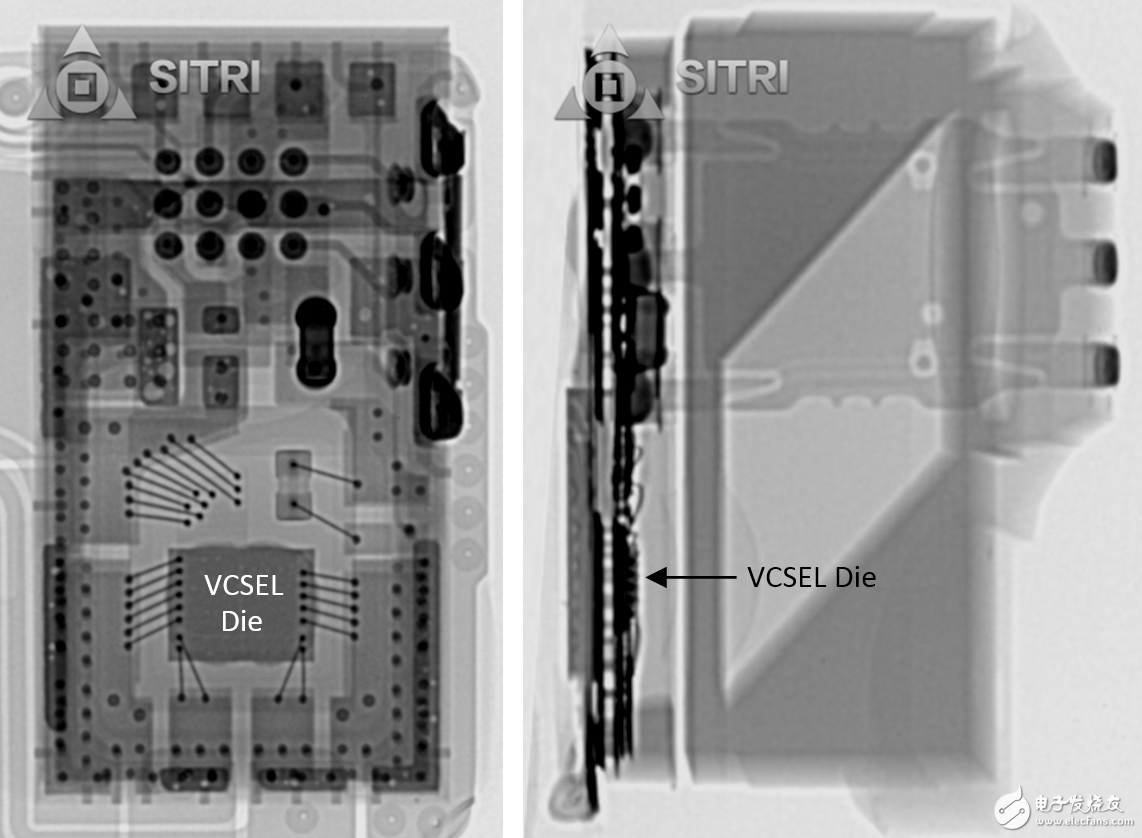
The entire module X-Ray photo
As shown in the above figure X-Ray, the VCSEL chip functions as a flood light (emitting infrared light).
distance sensor
As mentioned above, the distance sensor chip in the entire module comes from STMicroelectrics' ToF chip, which has been adopted in the iPhone 7+.
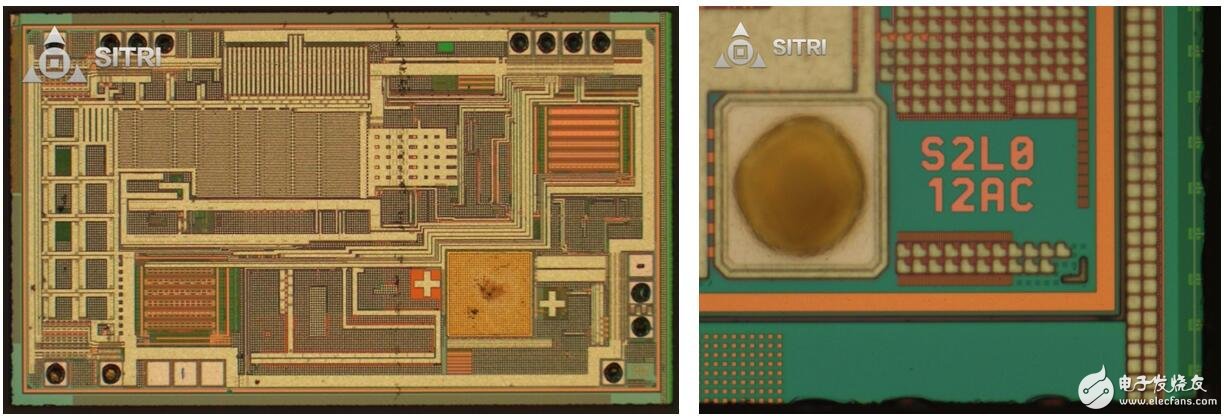
Distance sensing ToF chip - optical microscope
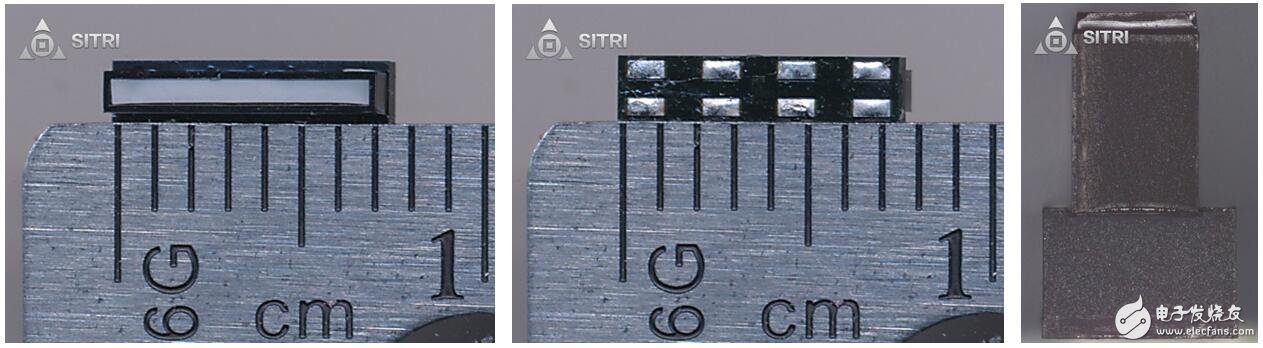
Ambient light sensor
The ambient light sensor of the iPhone X differs from the conventional ambient light sensor in its appearance as a flat and long shape, which may be caused by insufficient space, and a diffuser is also placed above the chip.
Ambient light sensor package scanning
Ambient light sensor package X-Ray photo
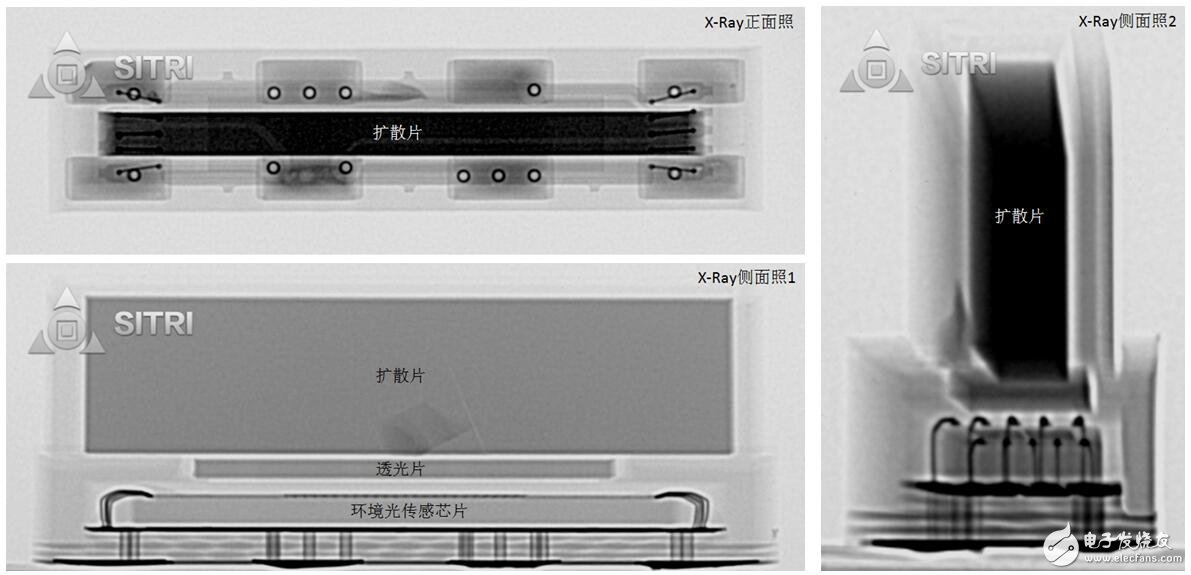
After removing the diffuser above, you can see the entire ambient light sensor chip and the glass transparent sheet above.

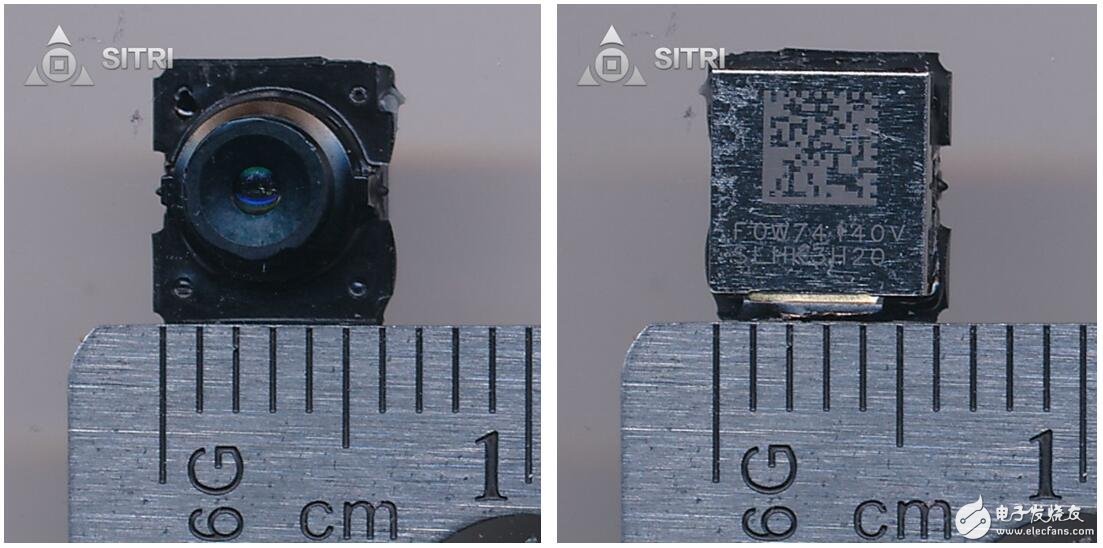
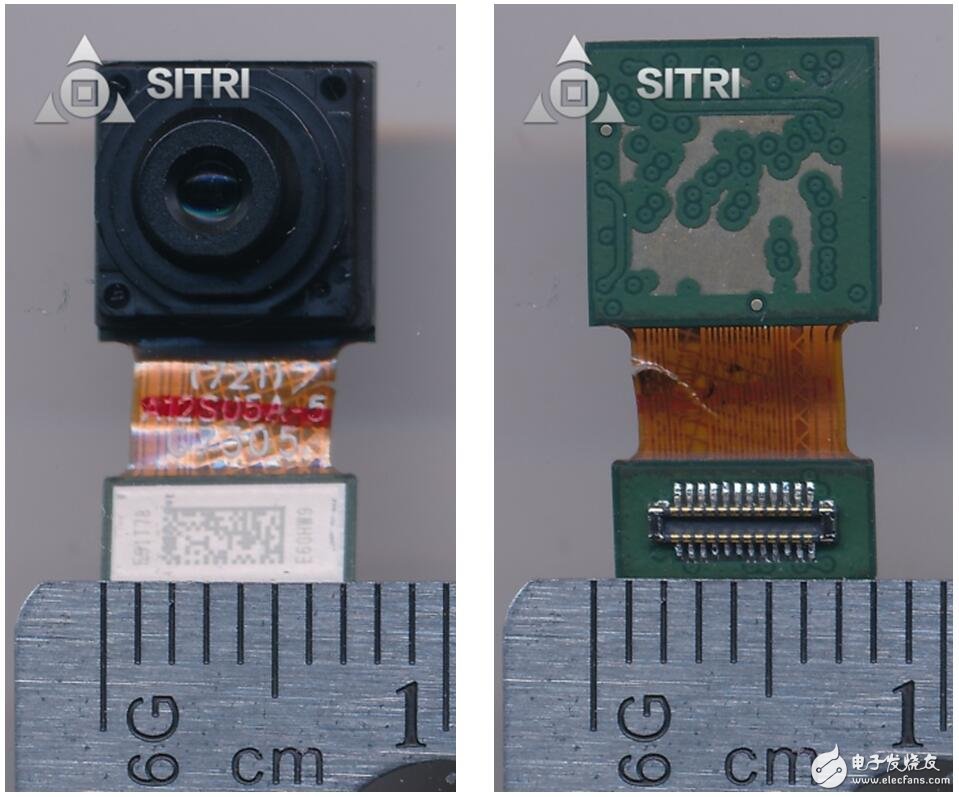
Front camera
Front camera scanning
Front camera X-Ray photo

Front camera optical microscope photo - Lens

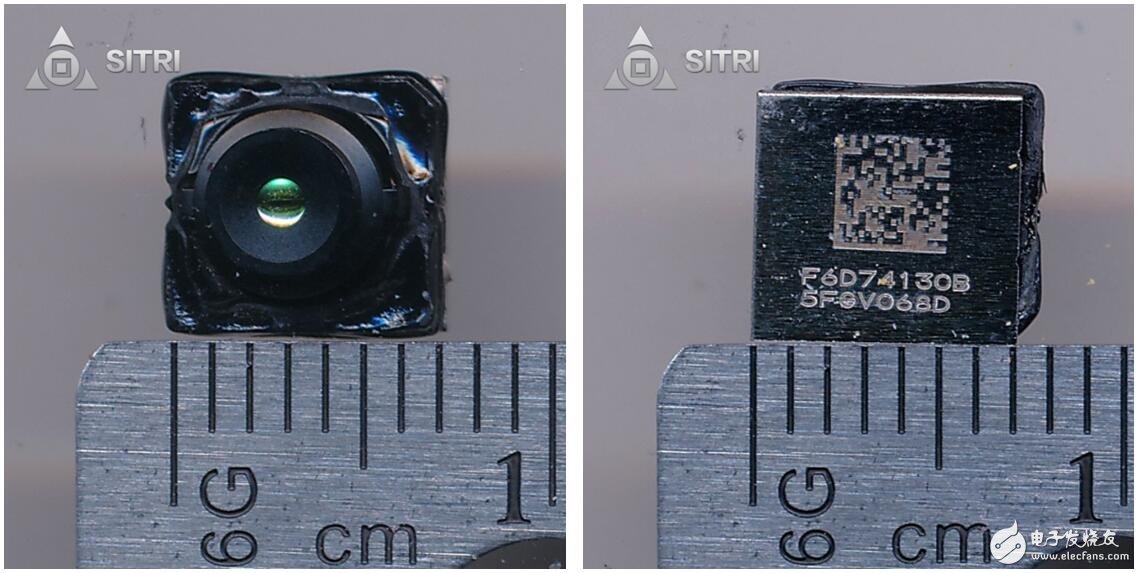
Infrared camera
Infrared camera scanning
Infrared camera X-Ray photo

Infrared camera optical microscope photo - Lens

In addition to these sensors, the iPhone X's face recognition is also a huge contribution to its powerful bionic processor A11.
A11 processor
A11 optical microscope
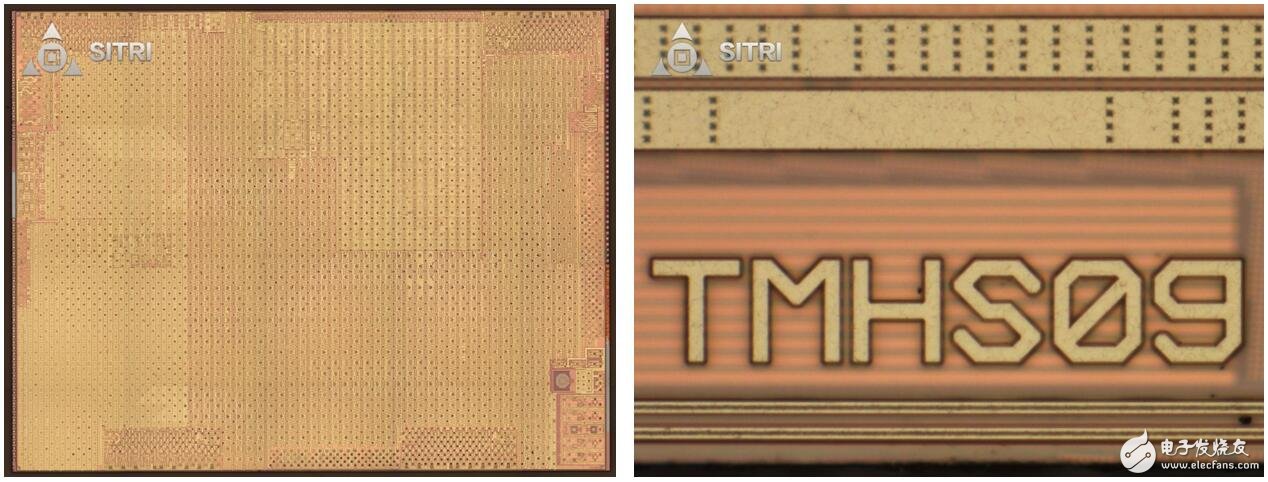
Apple's iPhone X's "Qi Liuhai" also has a microphone sensor from Lou's.
Microphone sensor
Microscope optical microscope
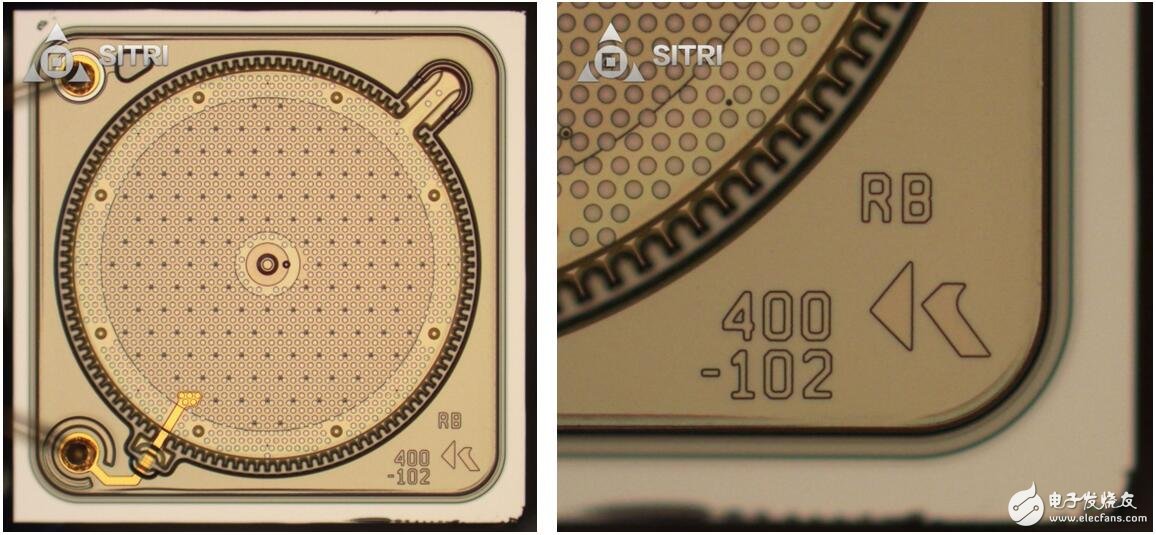
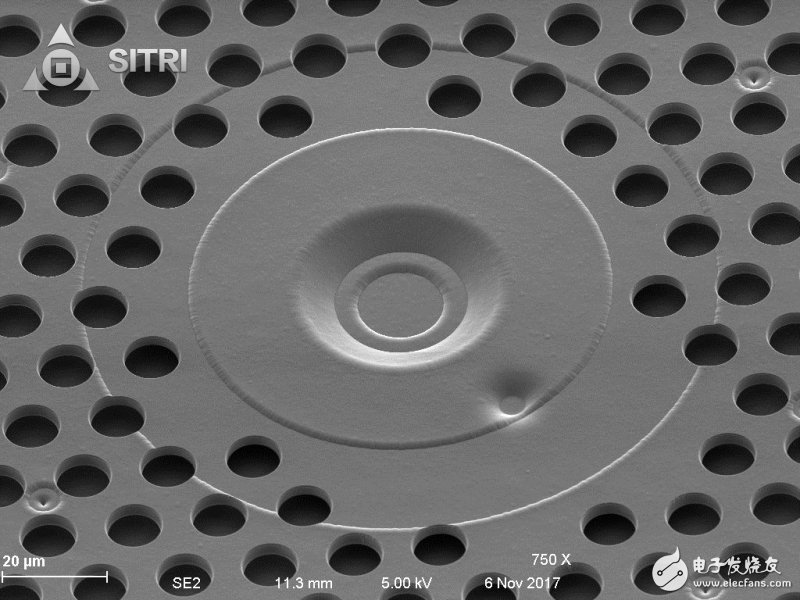
Microphone scanning electron microscope
After reading the "Xi Liuhai" of iPhone X, let's take a look at the sensors on the Vivo X20's face recognition function.
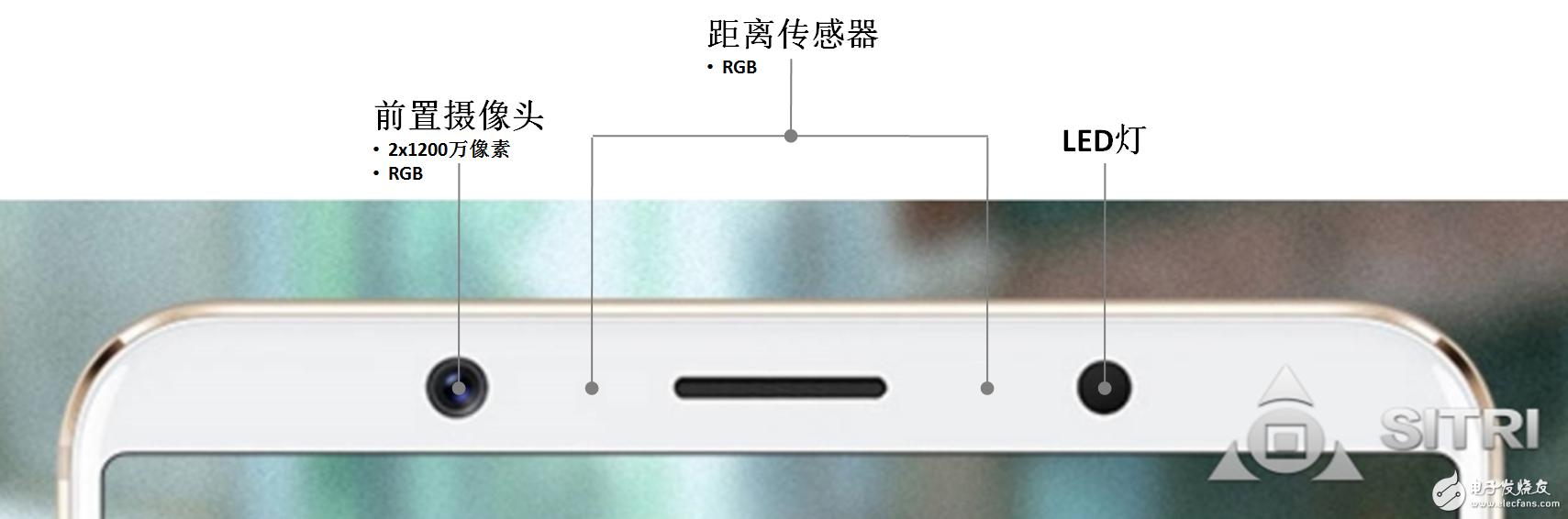
As shown above, the Vivo X20's face recognition sensor consists of a front camera and a distance sensor. Two of the distance sensors are the same type of chips, all from AMS. In particular, we found an LED light on the edge of a Vivo X20 sensor. I wonder if this is related to the Vlight X20's “backlighting is clear�
Vivo X20 machine structure
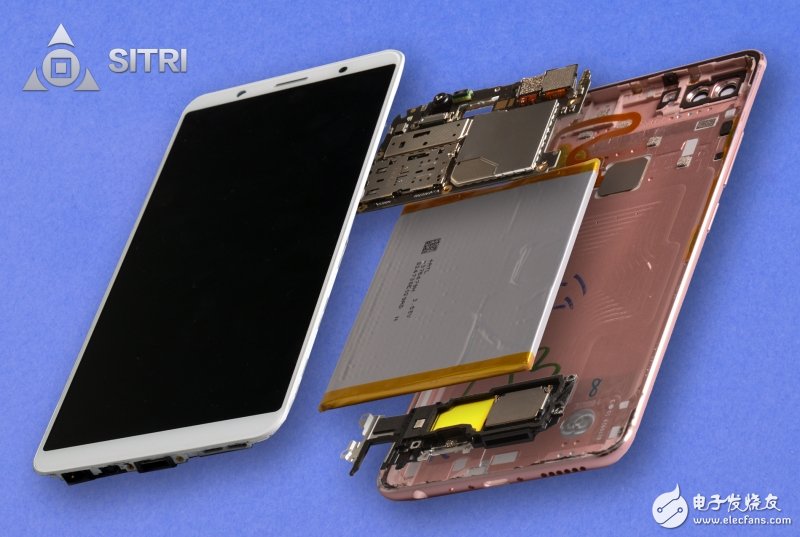

Vivo X20 main parts diagram
LED light
LED light microscope photo
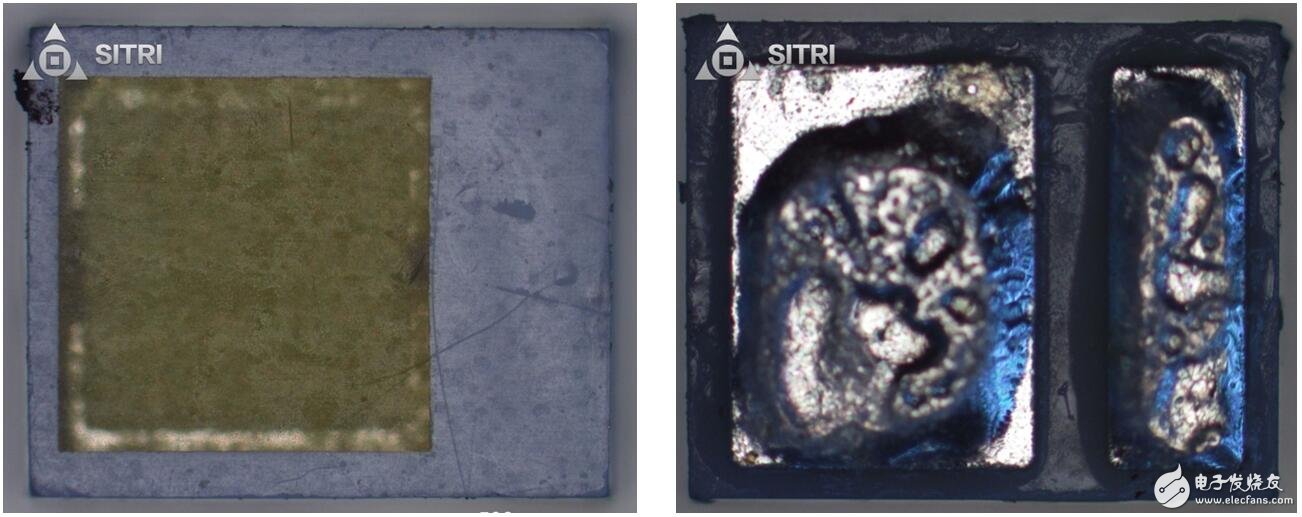
LED light X-Ray photo

distance sensor
Distance sensor optical microscope


Distance sensor X-Ray photo
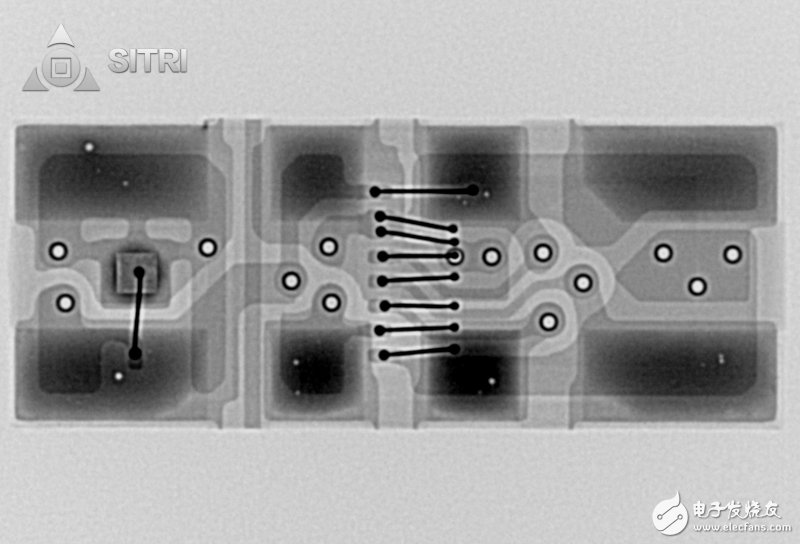
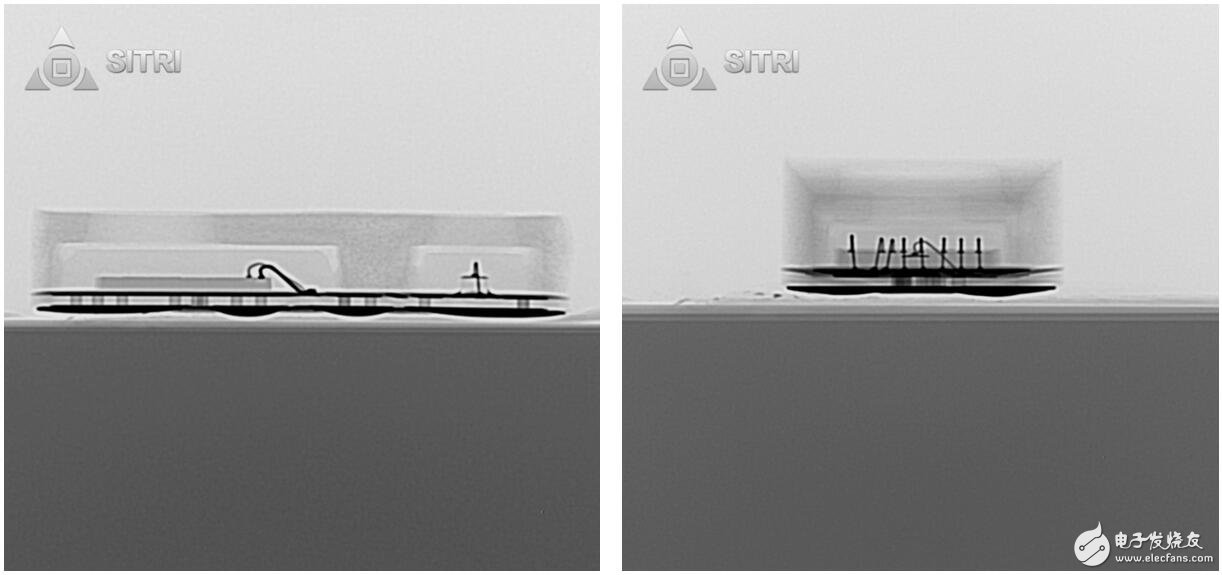
Front camera
Front camera module scanning
Front camera X-Ray photo

Front camera optical microscope photo - Lens
After reading the iPhone X and Vivo X20 sensors, I don't know if you have any further understanding of 3D face recognition? Subsequent SITRI will further analyze the other sensors and chips in these two phones.
External Cavity Tunable Laser,Laser Grating Sensor,Bragg Grating Stabilized Laser,Grating Stabilized Diode Laser
AcePhotonics Co.,Ltd. , https://www.acephotonics.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)