The Internet of Things has been identified as one of China's strategic emerging industries. The introduction of the "Twelfth Five-Year Development Plan for the Internet of Things" will undoubtedly bring a strong east wind to the developing Internet of Things in China, and RFID technology as a thing. The key technologies for the development of networking will definitely expand with the development of the Internet of Things.
RFID radio frequency identification technology
The full name of RFID in English is Radio FrequencyIdentification, radio frequency identification, also known as electronic tag, radio frequency identification, inductive electronic chip, proximity card, proximity card, contactless card, electronic bar code.
RFID radio frequency identification is a non-contact automatic identification technology. It automatically recognizes the target object and acquires relevant data through the radio frequency signal. The identification work can work in various harsh environments without manual intervention.
RFID technology can recognize high-speed moving objects and recognize multiple labels at the same time, which is quick and easy to operate. Short-range RF products are not afraid of harsh environments such as oil stains and dust pollution. Bar codes can be replaced in such environments, such as tracking objects on the assembly line of a factory. Long-range RF products are mostly used for transportation, and the recognition distance can reach several tens of meters, such as automatic charging or identification of vehicle identity.
RFID system architecture
A typical RFID system is mainly composed of a reader, an electronic tag, an RFID middleware, and an application system software. Generally, the middleware and application software are collectively referred to as an application system.
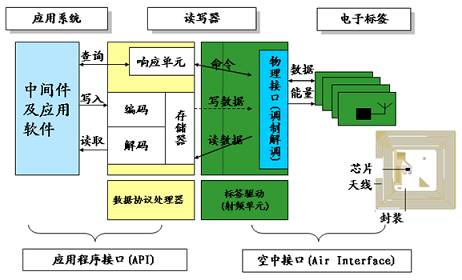
FRID system structure
In actual RFID solutions, RFID systems contain some basic components. Components are divided into hardware components and software components.
From the perspective of function realization, the RFID system can be divided into two parts: the edge system and the software system. The edge system mainly completes the information perception and belongs to the hardware component part; the software system completes the processing and application of the information; the communication facility is responsible for the entire RFID system. Information transfer.
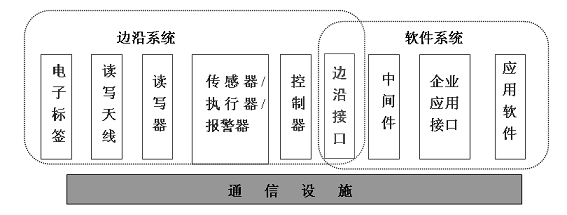
Basic components of radio frequency identification system
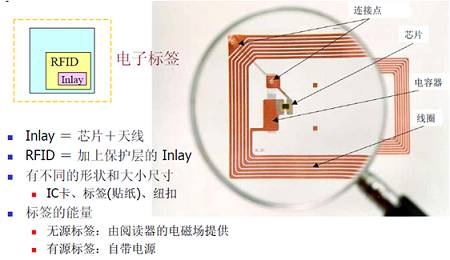
1, electronic label
Electronic Tag, also known as a transponder or Smart Label, is a miniature wireless transceiver that consists mainly of a built-in antenna and chip.
2, reader
A reader is a device that captures and processes RFID tag data. It can be a single individual or embedded in other systems. The reader is also one of the important components that make up the RFID system. Because it can write data into the RFID tag, it is called a reader.
The hardware part of the reader is usually composed of transceiver, microprocessor, memory, external sensor/actuator, alarm input/output interface, communication interface and power supply.
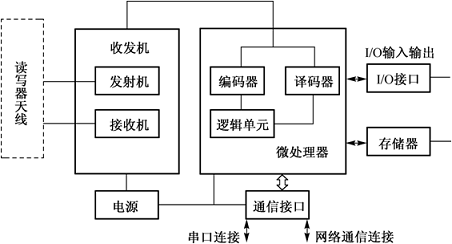
Reader composition diagram
3, the controller
The controller is the command center for the orderly operation of the reader chip. The main functions are:
Communicate with application system software;
Execute the action instructions sent from the application system software;
Control the communication process with the tag;
Encoding and decoding of baseband signals;
Perform an anti-collision algorithm;
Encrypting and decrypting data transmitted between the reader and the tag;
Perform identity authentication between the reader and the electronic tag;
Control of other external devices such as keyboards and display devices.
Among them, the most important is the control operation of the reader chip.
4, reader antenna
The antenna is a device that receives or radiates the power of the front-end RF signal in the form of electromagnetic waves. It is an interface device between the circuit and the space, and is used to realize the conversion of the guided wave and the free space wave energy. In the RFID system, the antenna is divided into two categories: an electronic tag antenna and a reader antenna, which respectively bear the functions of receiving energy and transmitting energy.
The characteristics of the RFID system reader antenna are:
Small enough to be attached to the item you need;
Directionality with omnidirectional or hemispherical coverage;
Capable of providing the chip with the largest possible signal;
Regardless of the direction of the item, the polarization of the antenna can match the interrogation signal of the card reader;
Robust
cheap price.
The main factors to consider when choosing a reader antenna are:
Type of antenna;
The impedance of the antenna;
The performance of the RF applied to the item;
The performance of the RF when there are other items surrounding the labelled item.
5. Communication facilities
Communication facilities provide secure communication connections for different RFID system management and are an important part of RFID systems. Communication facilities include wired or wireless networks and serial communication interfaces for readers or controllers to be connected to a computer. The wireless network can be a personal area network (PAN) (such as Bluetooth technology), a local area network (such as 802.11x, WiFi), or a wide area network (such as GPRS, 3G technology) or a satellite communication network (such as a synchronous orbit satellite L-band RFID system) .
The basic principle of RFID system
1, the basic principle
From the point of view of communication between electronic tags and readers and energy sensing, systems can generally be divided into two types, namely, Inductive Coupling system and Electromagnetic Backscatter Coupling system. Inductive coupling is achieved by spatial high-frequency alternating magnetic field, which is based on the law of electromagnetic induction; electromagnetic backscattering coupling, that is, the radar principle model, the emitted electromagnetic wave hits the target and then reflects, and carries back the target information, based on the electromagnetic wave. The law of spatial communication.
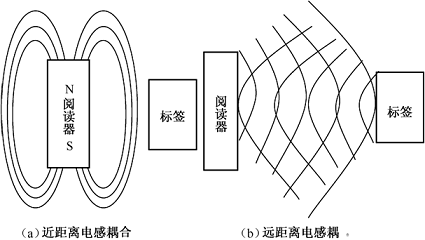
2. Inductively coupled RFID system
The inductive coupling of RFID corresponds to the ISO/IEC 14443 protocol. The inductively coupled electronic tag consists of an electronic data carrier, usually consisting of a single microchip and a large area coil used as an antenna.
Inductively coupled electronic tags are almost always passive, and all the energy required to operate the microchip in the tag is provided by the inductive electromagnetic energy sent by the reader. The high-frequency, strong electromagnetic field is generated by the antenna coil of the reader and passes through the cross-section of the coil and the space around the coil to induce electromagnetic induction of nearby electronic tags.

Working principle diagram of inductively coupled RFID system
3. Electromagnetic backscatter RFID system
(1) Backscatter modulation
Radar technology provides a theoretical and applied basis for RFID backscatter coupling. When an electromagnetic wave encounters a space target, part of its energy is absorbed by the target, and another part is scattered to various directions with different intensities. Of the scattered energy, a small portion is reflected back to the transmitting antenna and received by the antenna (so the transmitting antenna is also the receiving antenna), and the received signal is amplified and processed to obtain information about the target.
When electromagnetic waves are emitted from the antenna to the surrounding space, different targets are encountered. A portion of the electromagnetic wave energy reaching the target (free space attenuation) is absorbed by the target, and another portion is scattered in various directions with different intensities. A portion of the reflected energy will eventually return to the transmitting antenna, called an echo. In radar technology, this reflected wave can be used to measure the distance and bearing of the target.
For RFID systems, electromagnetic backscatter coupling can be used to perform data transmission from electronic tags to readers using electromagnetic wave reflection. This mode of operation is mainly used in systems with 915MHz, 2.45GNz or higher.
(2) RFID backscatter coupling
The frequency at which a target reflects electromagnetic waves is determined by the cross section of the reflection. The size of the reflection cross section is related to a range of parameters, such as the size, shape and material of the target, the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave, and the direction of polarization. Since the reflection performance of the target generally increases with increasing frequency, the RFID backscatter coupling method uses UHF and UHF, and the distance between the transponder and the reader is greater than 1 m. The reader/writer, transponder (electronic tag) and antenna form a transceiver communication system.
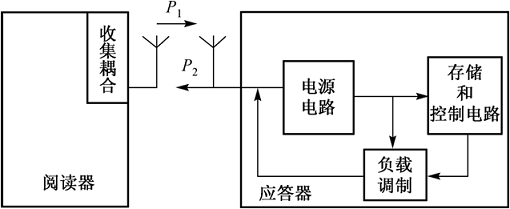
Principle of RFID backscatter coupling
4, the recognition principle of surface acoustic wave tags
(1) Surface acoustic wave device
Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) devices are based on piezoelectric effects and sound waves propagating at low speeds associated with surface elasticity. SAW devices are small in size, light in weight, high in operating frequency, wide in relative bandwidth, and can be fabricated in the same planar processing as integrated circuit processes, with simple manufacturing, high reacquisition and high design flexibility.
Surface acoustic wave devices have a wide range of applications, such as filters in communication devices. In RFID applications, the operating frequency of surface acoustic wave transponders is currently mainly 2.45 GHz.
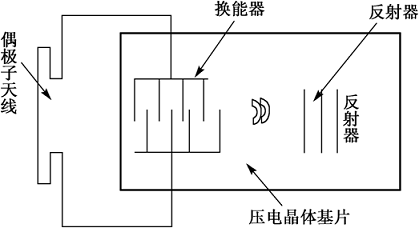
Basic structure of surface acoustic wave transponder
(2) Principle of surface acoustic wave RFID
The SAW tag consists of an interdigital transducer and a number of reflectors, the two buses of which are connected to the antenna of the electronic tag. The antenna of the reader periodically transmits a high frequency interrogation pulse, and within the receiving range of the electronic tag antenna, the received high frequency pulse is converted into a surface acoustic wave by the interdigital transducer and propagates on the surface of the crystal. The reflector composition partially reflects the incident surface wave and returns to the interdigital transducer, which in turn converts the reflected pulse train into a high frequency electrical pulse train. Due to the low propagation rate of the surface acoustic wave, the effective reflected pulse train returns to the reader after a lapse of a delicate delay.
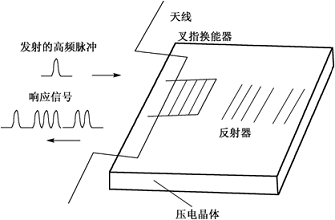
Surface acoustic wave propagation
(3) Key technologies of surface acoustic wave RFID systems
Tag coding capacity and action distance
Transponder and reader cooperation
Application of small, low-cost electronic tag antennas suitable for items to be identified
Package
Due to the wide variety of items and environments in which the labels are attached, the package structure has its own characteristics, and they must meet the following requirements.
Ensure that the piezoelectric chip can withstand external environmental stresses and their changes during the working life without causing performance degradation.
At least it cannot affect or rarely affect the high-frequency electromagnetic wave receiving effect of the tag antenna.
The method of fixing to the object to be identified is simple, firmly attached, and does not significantly damage the article.
Beautiful appearance, harmonious to the object to be identified, and meet the requirements of safety and environmental protection.
(4) Advantages of surface acoustic wave RFID
Because the SAW device itself works in the RF band, it is passive and has strong anti-electromagnetic interference capability. Therefore, the electronic tag realized by SAW technology has certain unique advantages and is complementary to integrated circuit (IC) technology.
The main features of SAW RFID are:
The reading range is large and reliable, up to several meters;
Can be used on metal and liquid products;
The matching between the tag chip and the antenna is simple, and the manufacturing process cost is low;
It not only recognizes stationary objects, but also recognizes high-speed moving objects at speeds up to 300km/h.
It can be used in harsh environments such as high temperature difference (-100 ° C ~ 300 ° C) and strong electromagnetic interference.
Advantages and disadvantages of RFID technology
1. Advantages:
RFID chips and RFID readers are highly resistant to substances such as water, oil and chemicals.
The reading of information is not limited by the size and shape of the chip, and it is not necessary to match the fixed size and printing quality of the paper for the purpose of reading accuracy. Moreover, the RFID tag is being developed in a small form and in various forms for application to different products. .
RFID technology recognition is more accurate than traditional smart chips, and the distance of recognition is more flexible. Penetration and barrierless reading can be achieved.
The RFID chip tag can repeatedly add, modify, and delete internally stored data to facilitate information update.
Internal data content is protected by passwords, making its content less susceptible to forgery and alteration.
The data capacity of the RFID chip is large, and as the technology develops, the capacity has an increasing trend.
2, disadvantages:
Technological maturity is not enough. RFID technology has a short time and is not very mature in technology. Due to the reverse reflective nature of UHF RFID tags, it is difficult to apply in metal, liquid and other commodities.
high cost. RFID electronic tags are relatively expensive compared to ordinary bar code labels, which are dozens of times larger than ordinary bar code labels. If the usage is large, the cost will be too high, which greatly reduces the enthusiasm of the market for using RFID technology.
Security is not strong enough. The security problems faced by RFID technology are mainly caused by illegal reading and malicious tampering of RFID electronic tag information.
Technical standards are not uniform. RFID technology has not yet formed a unified standard, and multiple standards coexist in the market, resulting in incompatible RFID tags of different enterprise products, which in turn causes confusion in the application of RFID technology to a certain extent.
Development status and prospects of RFID technology
With the continuous reduction of the cost of RFID equipment, the gradual unification of standards, the extensive application of digital information technology in various industries, and the expansion of scale application industry, RFID technology will have broader development prospects, and its potential value will be exerted. The RFID technology industry will gradually grow and mature.
1. Development history of radio frequency identification
RFID technology was born during World War II and was first used by the Royal Air Force to identify its own and allied fighters. In order to identify the returning aircraft, the United Kingdom equips the Allied aircraft with a radio transceiver. When the interrogator on the control tower transmits an interrogation signal to the returning aircraft, the transceiver on the aircraft receives the signal. A signal is sent back to the interrogator, which identifies the enemy and the enemy based on the received return signal. This is the first RFID identification system identified, and the first practical application of the first RFID.

Since then, RFID technology has also been applied to wildlife tracking, road toll systems and other fields. After the 1990s, with the rapid development of integrated circuit manufacturing and information technology, RFID technology has become increasingly mature, and its cost has become lower and lower, which has gradually attracted people's attention.
2. Development prospects of radio frequency identification
RFID radio frequency identification technology has gradually developed into an independent and interdisciplinary field of expertise. RFID RFID technology combines a large number of technologies from completely different fields of expertise (eg, high frequency technology, electromagnetic compatibility technology, semiconductor technology, data protection and cryptography, telecommunications technology, manufacturing technology, etc.).
In the past ten years, RFID radio frequency identification technology has been rapidly developed, and it has been widely used in many fields of traceability and anti-counterfeiting applications such as industrial automation, commercial automation, and transportation control management. With the advancement of technology, the types of products based on RFID radio frequency identification technology will become more and more abundant, and the application will become more and more extensive. It is expected that RFID radio frequency identification technology will continue to maintain rapid development momentum in the next few years.
In general, RFID radio frequency identification technology is currently developing towards standardization, low cost, low error rate, high security, and low power consumption.
standardization
Industry standards and related product standards are still not uniform. Electronic labels have not yet formally formed a unified (including various frequency bands) international standards.
low cost
At present, the lowest price of an electronic label in the United States is about 20 cents. Such a price cannot be applied to some single-piece products with lower value. Only when the unit price of the electronic label drops below 10 cents, it can be applied to the whole scale. The whole package of goods.
Low error rate
Although the single technology of RFID electronic tags has matured, the overall product technology is not mature enough, and there is still a high error rate (the ratio of RFID misreading is sometimes as high as 20%), and it is also needed in integrated applications. Overcome a lot of technical problems.
High security
The currently widely used passive RFID system does not have a very reliable security mechanism, and the data cannot be kept secret. The RFID data is also vulnerable to attack, mainly because the RFID chip itself and the chip are in the process of reading or writing data. Easy to be exploited by hackers.
Application fields of RFID technology
Access control: personnel access control monitoring management
Animal Monitoring: Animal Husbandry Management, Pet Identification, Wildlife Ecology Tracking
Transportation: Highway toll system
Logistics Management: Baggage identification, inventory, logistics and transportation management for air transportation
Automatic control: classification of automobile, home appliance, electronics industry, assembly line management
Medical applications: Hospital medical record system, instrumentation equipment management
Material Management: Automated inventory and control system for factory materials
Quality Tracking: Product Quality Tracking, Feedback
Resource recovery: management of pallets, recyclable containers, etc.
Anti-theft application: Anti-theft management in supermarkets, libraries or bookstores
Anti-counterfeiting: Anti-counterfeiting for brand-name tobacco and alcohol and valuables
Waste treatment: garbage collection and disposal, waste control system
Joint ticket: multi-purpose smart stored value card, card, etc.
Dangerous goods: Ordnance firearms, detonator explosive control
RFID will build a bridge between the virtual world and the physical world. It is foreseeable that in the near future, RFID technology will not only be widely adopted in various industries, but eventually RFID technology will be integrated with ubiquitous computing technology and have a profound impact on human society.
As a global manufacturing base, China will be the world's largest RFID application market in the future. This will be a rare opportunity for domestic research institutions and enterprises.
36W Interchangeable Power Adapter
36W Interchangeable Power Adapter,Univeral Power Adapter 24V1.5A,12V3A 36W Interchangeable Plug Power Adapter,Exchangeable Plug Power Adaptor 12V3A
Guangdong Mingxin Power Technologies Co.,Ltd. , https://www.mxpowersupply.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)