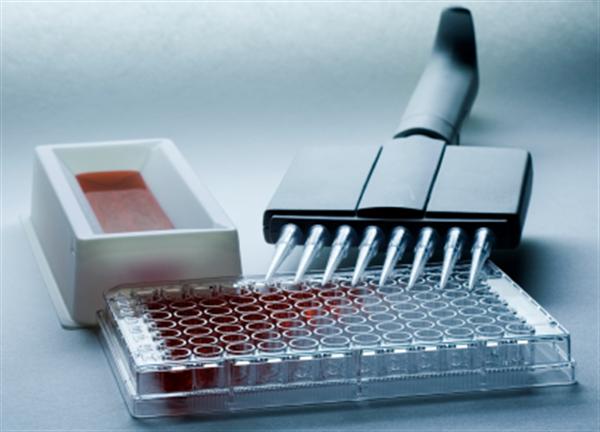
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) is a widely used technique in biological and medical research for detecting and quantifying specific substances, such as proteins, antibodies, and antigens. According to Shanghai Jinma's analysis, the ELISA kit combines the specific reaction between antigens and antibodies with the high-efficiency catalytic activity of enzymes on substrates. The antigen-antibody interaction occurs in the wells of a solid-phase carrier—typically a polystyrene microtiter plate. After each reagent is added, excess unbound components are removed through washing, ensuring accurate and reliable results. This method also provides good stability and reproducibility.
In practical applications, there are several variations of ELISA methods based on the type of target being detected. These include: the indirect method for detecting antibodies (Panel A), the sandwich method for detecting antigens (Panel B), and the competitive method for detecting small molecules or haptens. Each method has its own advantages and is chosen depending on the experimental requirements.
Based on years of research experience, Shanghai Jinma Biological recommends using the double antibody sandwich method and the indirect ELISA method due to their reliability and accuracy. Here are six key steps for conducting an ELISA experiment:
- Capture Antibody Coating: Dilute the capture antibody to a concentration of 1–10 μg/ml in 0.05 M carbonate coating buffer (pH 9.6). Add 0.1 ml per well of a polystyrene plate and incubate overnight at 4°C. The next day, discard the solution and wash the plate three times with washing buffer (3 minutes each time).
- Sample Addition: Add 0.1 ml of the diluted sample to each coated well. Incubate at 37°C for 1 hour. Include blank, negative, and positive control wells during this step.
- Add Enzyme-Labeled Antibody: Add 0.1 ml of freshly prepared enzyme-conjugated antibody (diluted appropriately) to each well. Incubate at 37°C for 30–60 minutes, then wash again.
- Add Substrate: Add 0.1 ml of TMB substrate solution to each well and incubate at 37°C for 10–30 minutes. The color development indicates the presence of the target molecule.
- Stop the Reaction: Add 0.05 ml of 2M sulfuric acid to each well to stop the enzymatic reaction.
- Result Interpretation: Observe the color change visually against a white background. A darker color indicates a stronger positive result. Alternatively, measure the optical density (OD) at 450 nm (or 410 nm if ABTS is used) using an ELISA reader. If the OD value exceeds 2.1 times the negative control, it is considered positive.
We are committed to providing our customers with high-quality ELISA kits and comprehensive technical support. With extensive experience, excellent product quality, and a wide inventory, we ensure timely delivery and competitive pricing. Our goal is to deliver the best service and support for all your experimental needs.
Currently, we are offering special promotions on all ELISA kits with significant discounts. We also provide free technical guidance and testing services. Whether you're a new or returning customer, feel free to reach out for more details.
Digital Signage in Bank,Signage Screen,Digital Signage Advertising,Smart Digital Signage
Guangdong Elieken Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.elieken.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)