The crossover slope (also called the attenuation slope of the filter) is used to reflect the falling slope of the frequency response curve below the crossover point, expressed in decibels/octave (dB/oct). It has one-order (6 dB/oct), second-order (12 dB/oct), third-order (18 dB/oct), and fourth-order (24 dB/oct) points. The higher the order, the frequency after the crossover point. The greater the slope of the curve. More commonly used is the second-order crossover slope. Higher-order dividers can increase the slope, but have a large phase shift; lower-order dividers can produce a smoother slope and a good transient response, but have poorer amplitude-frequency characteristics. This article first introduced the type and principle of the divider, followed by a detailed description of what the slope of the divider is and what the important role of the slope, the specific follow Xiaobian together to find out.
Type of dividerAccording to the circuit connection of each unit in the divider, it can be divided into: series divider and shunt divider. Nowadays, parallel tap dividers are mainly used in the industry.
The advantage is that in a multi-way speaker, each can be considered as a separate part. If a series divider is used, any one of the parts may affect the high-pass and low-pass characteristics. All car audio applications are parallel dividers.
According to the level of the level of points, can be divided into high-level divider and low-level divider. The high-level divider is also commonly referred to as a passive divider, which refers to a high-power signal amplified by a power amplifier and processed by a passive divider to be output to a specific unit. A low-level divider, also known as an active divider, consists of an active electronic high-pass, low-pass, or band-pass filter and is typically implemented in the host, pre-processor, or preamplifier of the power amplifier.
The frequency divider is divided into rebroadcast frequency bands, which can be divided into high-pass, band-pass, and low-pass dividers. The divider's electronic components and the slope of the attenuation can be divided into first-order, second-order, third-order, and fourth-order points. Frequency device.
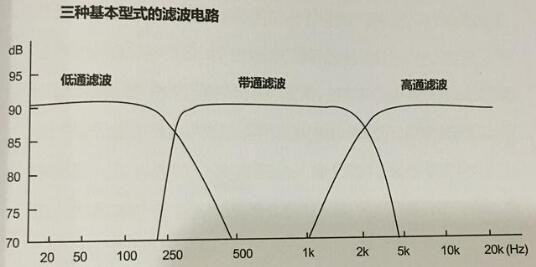
The divider circuit of the speaker system is composed of L/C filters (inductors and capacitors). The parallel divider design mainly uses three basic filters.
The form, their response characteristics as shown in the figure, they are: low-pass filter, the attenuation of the high frequency band, usually used in woofer; band-pass filter, the high-frequency end and low-end attenuation, generally used in the middle The unit; high-pass filter, attenuation of low frequency, most of the use of tweeter.
The filter can usually be described by three basic characteristics: the slope of the attenuation, the center frequency of the filter, and the Q value. The slope is generally at every octave (octave)
Decrease in dB/Octave. When L and C are combined by different circuit configurations, the slope of the filter can form an attenuation of 6, 12, 18, 24 dB per octave. A crossover network with more than 24 dB of attenuation is rarely used in passive crossover networks and is often used in active electronic crossover. These attenuation rates can also be expressed in terms of the slope order: first order is 6dB/Octave, second order is 12dB/Octave, third order is 18dB/Octave, fourth order is 24dB/Octave, and so on.
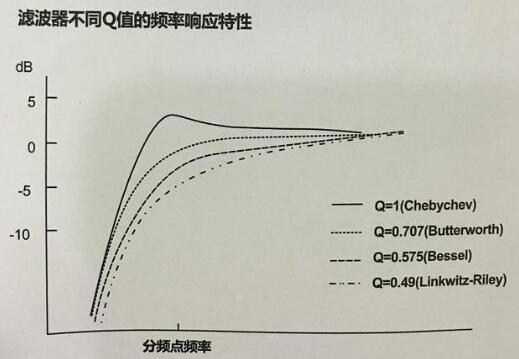
Frequency response characteristics of filters with different Q values
The circuit resonance frequency of the filter is the frequency of the frequency division point, which is the product of the inductance L and the capacitance C. Different combinations of L and C values ​​can give different responses.
The Q value of the filter has the same relationship with the Q value of the horn unit and the Q value after the unit is boxed. The Q value is a parameter that describes the curve change at the frequency division point.
Quantity. Different filter Q values ​​depict different attenuation response curves. Different response curves have different characteristics. They are named after the first engineer who discovered these response characteristics. For example: Chebychev (Q=1), Butterworth (Q=0.707), Bessel (Q=0.58), Linkwitz-Rily (Q = 049); The higher the Q, the sharper the change around the crossover point, the steeper the curve response; otherwise the smoother, smoother.

The crossover slope of the divider is also its attenuation slope, which is usually expressed in decibels per octave attenuation. The frequency is one octave up or down between the straight sections of the attenuation curve from the crossover point. The decibel value of the signal attenuation.
For example, when the signal frequency is decreased from 2000Hz to 1000Hz, the signal is attenuated by 6dB. According to the number of reactance elements used in each filter, the frequency divider can be divided into first, second, third and fourth order frequency dividers. The attenuation characteristics of signals other than the crossover slope are determined by the reactance elements used in each filter. The more reactive elements that each filter uses, the greater the attenuation slope. The divider will have more attenuation of the signal outside the crossover slope.
The first-order divider uses only one inductor or one capacitor per channel and has an attenuation slope of 6dB/oct;
The second-order frequency divider uses an inductance coil and a capacitor for each channel, and the attenuation slope is 12dB/oct;
Three and four reactance elements are used for each channel of the third and fourth-order frequency dividers, respectively, and the attenuation slopes are 18dB/oct and 24dB/oct, respectively. The most used ones are the first-order (6dB/oct) and second-order ( 12dB/oct) divider.
The third-order and fourth-order frequency dividers have large attenuation slopes and steep curves, which can reduce the signal overlap between the two loudspeakers, which is beneficial for reducing the phase distortion of the loudspeakers and improving the power capability of the loudspeakers.
The first-order and second-order frequency dividers attenuate the signal more slowly, which is beneficial to improve the transient response of the speaker. Therefore, the crossover frequency and attenuation frequency of the speaker must be determined based on their own preferences, performance specifications of the speaker and requirements for the use of the entire speaker.

The work of the divider seems simple, but it is not.
On the one hand, resistors, capacitors, and inductors interact with each other on the circuit. On the other hand, the speaker impedance varies with frequency, making it difficult to obtain the ideal crossover frequency response curve. The theoretical high-pass filter frequency response is compared to the actual simple high-pass network and it does not actually include the effect of the tweeter on the crossover network.
We are already familiar with the general method of dividing the audio signal of the input speaker into different frequency bands. There is no doubt that this is only an important task for the frequency divider. To feed the speaker with an audio signal of a suitable frequency band was once a measure of the frequency divider operation. On the basis of good and bad, people have been exploring to make the frequency divider have the same flat frequency response and stable attenuation slope as textbook filters. It seems that as long as the divider and speaker are in their best working condition, both of them The synthesized frequency response must also be optimal. In fact, this situation is hard to happen.
The development of computer simulation technology enables us to more accurately and more precisely predict and maximize the use of electro-acoustic characteristics of loudspeakers, enabling us to use the geo-electrical characteristics of crossover networks to compensate for the frequency response of a particular loudspeaker. In the past, people always aim at theoretically perfect frequency response of the frequency divider, ignoring the acoustic characteristics of the speaker. Now, instead of paying attention to the synergy between the electrical performance of the frequency divider and the sound performance of the speaker, when determining the sound quality of the speaker, The frequency divider and the speaker are often considered equally important, so the total frequency response of the cabinet is the result of the divider's repair on the circuit and the actual acoustic response of the loudspeaker.
If the input sound pressure of a low-frequency loudspeaker is relatively prominent at the low-frequency end, but the upper end of the frequency is slightly depressed, this defect of the low-frequency loudspeaker is compensated by the design of the frequency divider. The divider can also be used to repair the overall performance of the speaker. The divider circuit can adjust the delay and phase of the audio signal in each band so that the output sound pressure of each speaker can be coincided in the room by changing the phase response of the divider. , Frequency divider, and choose the appropriate speaker aperture and speaker position between each other, will inevitably get the best speaker frequency response characteristics.
Aluminum Alloy Die Casting,Injection Mold,Alloy Die Casting,Glass Door Die Casting
Dongguan Metalwork Technology Co., LTD. , https://www.diecast-pro.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)