
This article is produced by NetEase Smart Studio (public number smartman 163). Focus on AI and read the next big era!
[Netease Smart News October 20 news] Looking back at history, you will find that the financial industry is the most difficult to achieve change. But inevitably, big banks and start-up companies still have made tremendous breakthroughs in the financial industry. I don’t think it’s because they use any particular technology, but because of their inherent cultural differences, diverse structural rigidity and Other cost-effective business models.
Financial innovation: too much empty talk, too little action
In other words, banks do not innovate because they are too large to adapt quickly and follow external incentives, or because they do not know how (or want) to actually change. Not only in the financial industry, but also in academia. Until the mid-1990s, there was no breakthrough in financial innovation. In fact, in a few survey literatures (Cohen and Levin, 1989; Cohen, 1995), more than 600 different articles and books have been cited, but none of them are related to financial innovation.
Of course, in the past five years, the situation has changed, but I think that this change is passive, not from the voluntary promotion of the banking industry.
Therefore, financial innovation seems to be usually introduced by the outside world rather than internally generated, and it is often more product innovation than process innovation (though I think this view is more controversial). Given the new technology paradigm (which is strengthening the strong causal relationship between innovation and growth), it seems natural to wonder whether a better model of innovation can be introduced by different industries.
I have found a very special and interesting example. The industry must “innovate and survive†rather than “innovation growthâ€: that is, the biopharmaceutical industry (Baker, 2003; Gans and Stern, 2004; Fuchs and Krauss, 2003; Lichtenthaler, 2008).
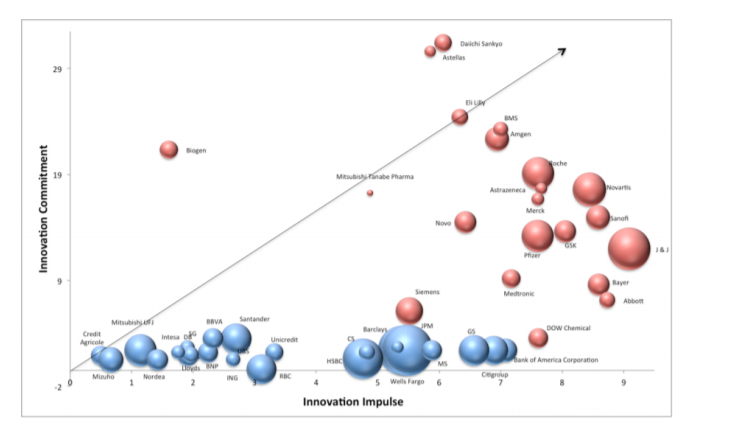
Innovation Transfer: Biopharmaceutical Industry
The biopharmaceutical industry is not a single industry, but includes two different technology areas: biotechnology, consisting of small companies that have driven research and exploration; and pharmaceutical companies that have become large in the last century. Listing and sales companies.
So, part of it is pure (high-risk) innovation, and the other part is purely commercial skills... It's something we've already seen, isn't it? The biopharmaceutical industry and the financial industry have formed a marked polarization
The characteristic of the biopharmaceutical industry is that the risks are mainly in the initial development process, not in the market sales stage. The problem is not to satisfy the needs of customers, nor to find a market for your products, but to develop this drug molecule first. The probability of success is very low, the timeline is very long (10-15 years), and 20 years of patent rights is only a short-term advantage. More importantly, only about two-thirds of the drugs can offset development costs, and most companies are losing money. The top 3% of the companies' profits account for almost 80% of the entire industry's profits. This is a difficult time. Business.
The biopharmaceutical industry is no longer just a labor-intensive industry, but an industry that requires a lot of capital investment. Innovation is not an add-on, but the cornerstone of a company's survival and development. This is why they must determine a series of different methods to promote their development - innovation: R & D, competitive cooperation programs, venture capital, joint ventures, acquisitions, limited partnership agreements, etc.
So far, my goal should be clear: the financial industry has not felt strongly about the need for innovation like the biopharmaceutical industry, and it has not tried and promoted the creation of new models to maximize its benefits.
Introducing Artificial Intelligence, your personal financial disrupter
Now you may still think like this: "Innovation is really great, but financial industry and biopharmacy are very different industries." So why should I insist on introducing innovation models from other industries? Well, this is the problem: I don't Think they are different.
And they are becoming more and more similar precisely because of artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence is injecting a powerful innovation into the financial industry. It has a development cycle and features that are similar to those in the biopharmaceutical industry: it takes a long time to be created, implemented and properly deployed (of course, The standards of the financial industry are consistent; it is highly technical and requires highly specialized talent; it is highly uncertain because you need to conduct a lot of experimentation before finding a workable solution, and artificial intelligence is being given to the financial industry. Bring huge pressure for innovation.
But artificial intelligence has also brought new development speed and credibility to the financial industry, reducing similar errors in the biopharmaceutical industry. It is very easy if your algorithm points out the wrong product or the wrong book that was recommended. If your system incorrectly interprets certain signals on the market, or if you make a mistake while developing a drug, you will lose millions of dollars in a matter of seconds and you may even lose your life.
As a result, it not only extends issues that are inherently financial in nature, such as regulation or accountability, but also introduces new issues such as biased data or lack of transparency (especially in consumer applications).
Finally, artificial intelligence poses a problem for “building a vs purchaseâ€, which is even larger than in the biopharmaceutical industry in the 1990s, reaching the peak in the current biotech pharmaceutical dichotomy (if you want to know, this The focus of your choice is on your data capacity, team and project scalability, and the uniqueness of the projects related to your competitors – do you have enough data to train an ANI? Is your team/project size sufficient? Is the ANI unique? Does your companion do something?)
Artificial intelligence is driving an ancient industry innovation that has a history of hundreds of years. This is why I believe that the introduction of artificial intelligence in the financial services industry is very important—for the specific innovations or products it introduces, it is not too much, because it is completely changing an industry innovation process that has hundreds of years of history.
Artificial intelligence segmentation in financial technology
Artificial intelligence is using structured and unstructured data in financial services to improve customer experience and customer engagement. In this way, abnormal values ​​and anomalies are discovered, revenues are increased, costs are reduced, predictable patterns are found, and improvements are made. Predicted reliability... But is it the same in other industries? The answer is obvious. So what's so special about artificial intelligence in the financial services industry?
First, the financial industry is an industry that requires a lot of data. You may think that these data are mainly concentrated in the hands of large financial institutions, but most of the data is public, and with the new EU Payment Directive (PSD2), larger databases can also be used by smaller companies. Artificial intelligence is easy to develop and apply because its access threshold is relatively low compared to other industries.
Second, many basic processes can be automated relatively easily, and many other processes can be increased by step-by-step calculations or speeds. Historically, artificial intelligence is one of the industries that most need such innovation. The competition is fierce and it is always looking for new sources of investment. Summary: The marginal impact of artificial intelligence is greater than in other areas.
Third, the transfer of wealth among different generations has made this area a truly “fertile ground†for the development of artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence requires a large amount of new data, and most importantly, some improved feedback information. After 00, it is not only willing to use artificial intelligence, but also can provide feedback information, but they obviously do not care about privacy and disclose their own data.
Of course, artificial intelligence in finance also faces a series of specific challenges that hinder the smooth and rapid implementation of smart finance: legacy systems that do not communicate with each other; data isolation; poor data quality control; lack of expertise; Lack of cultural mentality to adopt this technology.
Therefore, what is lacking at present is only an overview of the field of artificial intelligence financial technology. There are also many maps and categorizations of artificial intelligence financial technology start-up companies, so I did not introduce any new things here but just show you my personal classification:
Financial health: This type of application is designed to make end-users' lives better and more convenient. It also includes personalized financial services; credit scores; automated financial advisors and planners who help users make financial decisions (robo- - consultants, virtual assistants and chat bots; smart wallets can guide users in different ways according to the user's habits and needs.Typical examples include robotic consultants and dialog interfaces: Kasisito;Trim;Penny;Cleo;Acorns;Fingenius;Wealthfront; SigFig; Betterment; LearnVest; Jemstep; Credit Score Application: Aire; TypeScore; CreditVidya; ZestFinance; Applied Data Finance; Wecash;
Module chain: I think that given the importance of this tool, it should have a separate classification, regardless of the specific application (possibly payment, compliance, transactions, etc.). Typical applications include: Euclid; Paxos; Ripple; Digital Asset;
Financial security: This can be divided into identification (payment security and physical identification - biometrics and KYC) and detection (tracking fraud and abnormal financial behavior - AML and fraud detection). Such applications include: EyeVerify; Bionym; FaceFirst; On?do; and Feedzai; Kount, APEX Analytics;
Transfer of funds: This category includes payments, p2p loans, and debt collection. Such applications include: TrueAccord; LendUp; Kabbage; LendingClub;
Capital Markets: This is a big segment and I tend to divide it into five major modules:
1) Trading (trading or trading platform). Examples include: Euclidean; Quantestein; Renaissance Technologies, Walnut Algorithms; EmmaAI; Aidyia; Binatix; KimerickTechnologies; Pit.ai; Sentient Technologies; Tickermachine; Walnut Algorithm; Clone Algo; Algoriz; Alpaca; Portfolio123; Sigopt;
2) Self-funding (crowdfunding or housing transactions). Examples include: Senti?; Numerai; Quantopian; Quantiacs; QuantConnect; Inovance;
3) Market Intelligence (information extraction or insight generation). Examples include: Indico Data Solutions; Acuity Trading; Lucena Research; Dataminr; Alphasense; Kensho Technologies; Aylien; I Know First; Alpha Modus; ArtQuant;
4) Alternative data (Most alternative data applications are in the capital market, not in the broader financial sector, so it makes sense to put it here). Examples include: Cape Analytics; Metabiota; Eagle Alpha;
5) Risk Management (In most cases, this part of the startup also involves other modules). Examples include: Ablemarkets; Financial Network Analysis.
in conclusion
From the very beginning of the article, I have been insisting that artificial intelligence is making financial services increasingly similar to biopharmaceuticals, and that the financial industry may be able to learn something from the innovations of other industries. The reality is that the financial industry still needs to overcome some difficulties and challenges.
The biggest difference I see so far is the impact of AI on the physical product market. Artificial intelligence is making this industry more digital than ever before. Its ultimate goal is to create future banks: no branches, no credit cards, no fraud. A banking platform with modular components that can improve our financial literacy and eliminate the need to purchase physical products.
This is definitely a desirable new world. I can't wait.
references
Baker, A. (2003). "Biotechnology's Growth-Innovation Paradox and the New Model for Success". Journal of Commercial Biotechnology 9 (4): 286–88.
Cohen, W. (1995). "Empirical Studies of Innovative Activity", in Handbook of the Economics of Innovation and Technological Change, edited by Paul Stoneman. Cambridge, Mass.: Blackwell. Ch. 6, 182–264.
Cohen, W., Levin, R. (1989). "Empirical Studies of Innovation and Market Structure", in Handbook of Industrial Organization, Vol. 2, edited by Richard Schmalensee and Robert Willig. Amsterdam: North-Holland. Ch. , 1059–1107.
Frame, WS, White, LJ (2002). "Empirical studies of nancial innovation: lots of talk, little action?". Working Paper, Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, N. 2002–12.
Fuchs, G., Krauss, G. (2003). "Biotechnology in Comparative Perspective". In: Biotechnology in Comparative Perspective. G. Fuchs (ed.). New York: Routledge, 1–13.
Gans, J., Stern, S. (2003). "Managing Ideas: Commercialization Strategies for Biotechnology". Intellectual Property Research Institute of Australia Working Paper 01/03: 1–24.
Li, J., Halal, WE (2002). "Reinventing the biotech manager". Nature Biotechnology, 20 Suppl (6): 61–3.
Lichtenthaler, U. (2008). "Open Innovation in Practice: An Analysis of Strategic Approaches to Technology Transactions". IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 55 (1): 148–157.
Meyer, FJ (2002). "Business Models That Biotech Companies Employ". Enterprise Development KFBS Biotech Speakers Series
November 25, 2002
(Selected from: hackernoon compilation: NetEase See Compilation Robot Review: Rain Egg)
Pay attention to NetEase smart public number (smartman163), get the latest report of artificial intelligence industry.
9H Flexible Glass Screen Protector
This kind of Flexible Glass Screen Protective Film is made of nano-glass material and is an indispensable device for people who often drop their mobile phones. The Flexible Protective Film can be perfectly fixed on the mobile phone to completely protect the mobile phone screen to prevent scratches and cracks on the edge of the mobile phone screen.
The surface hardness is 9H hardness. Sharp objects (such as knives and keys) will not scratch the surface.
The high transparency of 0.22mm ensures that you can view all screen content clearly and clearly, while providing unique touch screen sensitivity.
The Screen Protection Film has an "oleophobic and waterproof" coating that prevents dust and fingerprint smudges and ensures that it can be easily removed.
In case the screen is damaged, the Screen Protector will break into small pieces that are not sharp, which is much safer than other glass screen protectors on the market.
If you want to know more about 9H Flexible Glass Screen Protector products, please click product details to view the parameters, models, pictures, prices and other information about 9H Flexible Glass Screen Protector products.
Whether you are a group or an individual, we will try our best to provide you with accurate and comprehensive information about 9H Flexible Glass Screen Protector!
9H Flexible Glass Screen Protector, 9H Screen Protector, 9H Flexible Protective Film, Flexible Protective Film
Shenzhen Jianjiantong Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.tpuprotector.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)