Data interaction between java and c/c++ - jni
I recently worked on a TIemsten database project using jni technology. In this project, we use java to write the interface and business logic, and use the c language to write the database odbc access. Simple odbc is actually not difficult, but data transfer between java and c is a cumbersome thing. There are several cases of data transfer between the two: the interaction of the basic data types between java and c, java to the object type to c, c to the object type returned to java, c call java class. The following is a description of several cases.
1, java to pass the basic data type to c
For basic data types, java and c correspond to each other, so they can be used directly. Their correspondence is;
Java type local type byte (bit)
Boolean jboolean 8, unsigned
Byte jbyte 8
Char jchar 16, unsigned
Short jshort 16
Int jint 32
Long jlong ​​64
Float jfloat 32
Double jdouble 64
Void void n/a
2.java pass object type to c
For the java object model passed in java, c should load the prototype of the java class, according to the corresponding c object, get the id of the java object method, and then call the java object method. For example: For example, there is a java class customer object passed to the c program as a jni parameter, and the customer has the method String getName().
JNIEXPORT jobject JNICALL Java_com_oracle_estt_sc_db_impl_SCQueryODBC__1getCustomer
(JNIEnv *env, jobject, jobject customer){
jmethodID methodId;
/ / Get the handle of the customer object
Jclass cls_objClass=env->GetObjectClass(customer);
/ / Get the id of the specific method getName in the customer object
methodId=env->GetMethodID(cls_objClass,"getName","()Ljava/lang/String;");
/ / call the specific method of the customer object getName
Jstring js_name=(jstring)env->CallObjectMethod(customer,methodId,NULL);
...
}
3.c return object type to java
In the c program, you first need to create the java object to be returned, get the id of each attribute, then assign a value to each attribute, and finally return. For example: the same customer object, there are attribute values ​​such as name, you need to assign a value to each property in the c program and return.
JNIEXPORT jobject JNICALL Java_com_oracle_estt_sc_db_impl_SCQueryODBC__1getCustomer
(JNIEnv *env, jobject, jobject customer){
......
/ / Found java Customer class, if it fails, the program returns
Jclass clazz = env->FindClass("com/oracle/estt/sc/busi/Customer");
If(clazz == 0)
Return 0;
/ / allocate memory for the new java class object obj
Jobject obj = env->AllocObject(clazz);
/ / Discover the properties in the class, if it fails, the program returns
jfieldID fid_id= env->GetFieldID(clazz,"customerID","I");
If (fid_id == 0)
Return 0;
jfieldID fid_name = env->GetFieldID(clazz,"name","Ljava/lang/String;");
If (fid_name == 0)
Return 0;
......
Env->SeTIntField(obj, fid_id, 1
Env->SetObjectField(obj, fid_name, jname);
......
Return obj;
}
4.c pass an array containing java objects to java
For this case, first get the size of the array, then take the object in the array, get the property value of the object or call the object method, save the obtained value to the local array, and then use the data flexibly. For example: java passes an array containing multiple customer objects to c, and decomposes the array in c and stores it in a local temporary array.
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_oracle_estt_sc_db_impl_SCInsertODBC__1insertCustomeRequest___3Lcom_oracle_estt_sc_busi_CustomerRequest_2
(JNIEnv *env, jobject, jobjectArray oa){
......
/ / Declare the customerrequest object
Jobject o_customer;
Int i;
jmethodID methodId;
Jint size=env->GetArrayLength(oa);
_tmp_bind[0]= (char *)malloc(size*sizeof(int));
_tmp_bind[1]= (char )malloc(size*sizeof(char)( 20 + 1));
...
/ / Copy the data of the input array into a temporary array
For(i=0;i
Micro motors Based on Dc Motor, micro motor belongs to the small size of dc motor,micro motor rotor, back cover, chassis, rotor winding is mainly copper, back cover most of the use of plastic material, motor shell use galvanized steel plate, the micro motor can be ROHS test.
A micro motor is any of a class of rotary electrical machines that converts direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy. The most common types rely on the forces produced by magnetic fields. Nearly all types of micro motors have some internal mechanism, either electromechanical or electronic, to periodically change the direction of current flow in part of the motor.
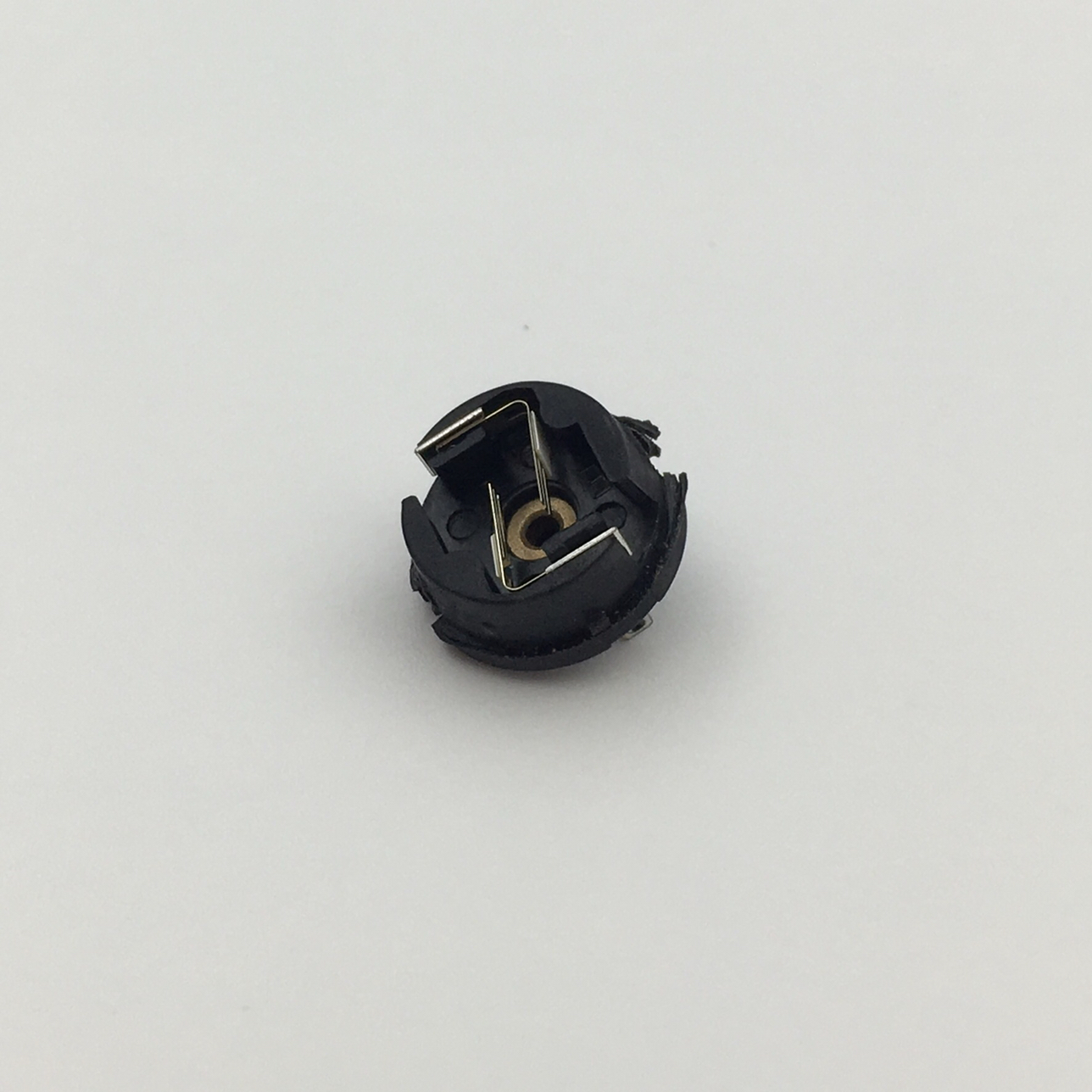
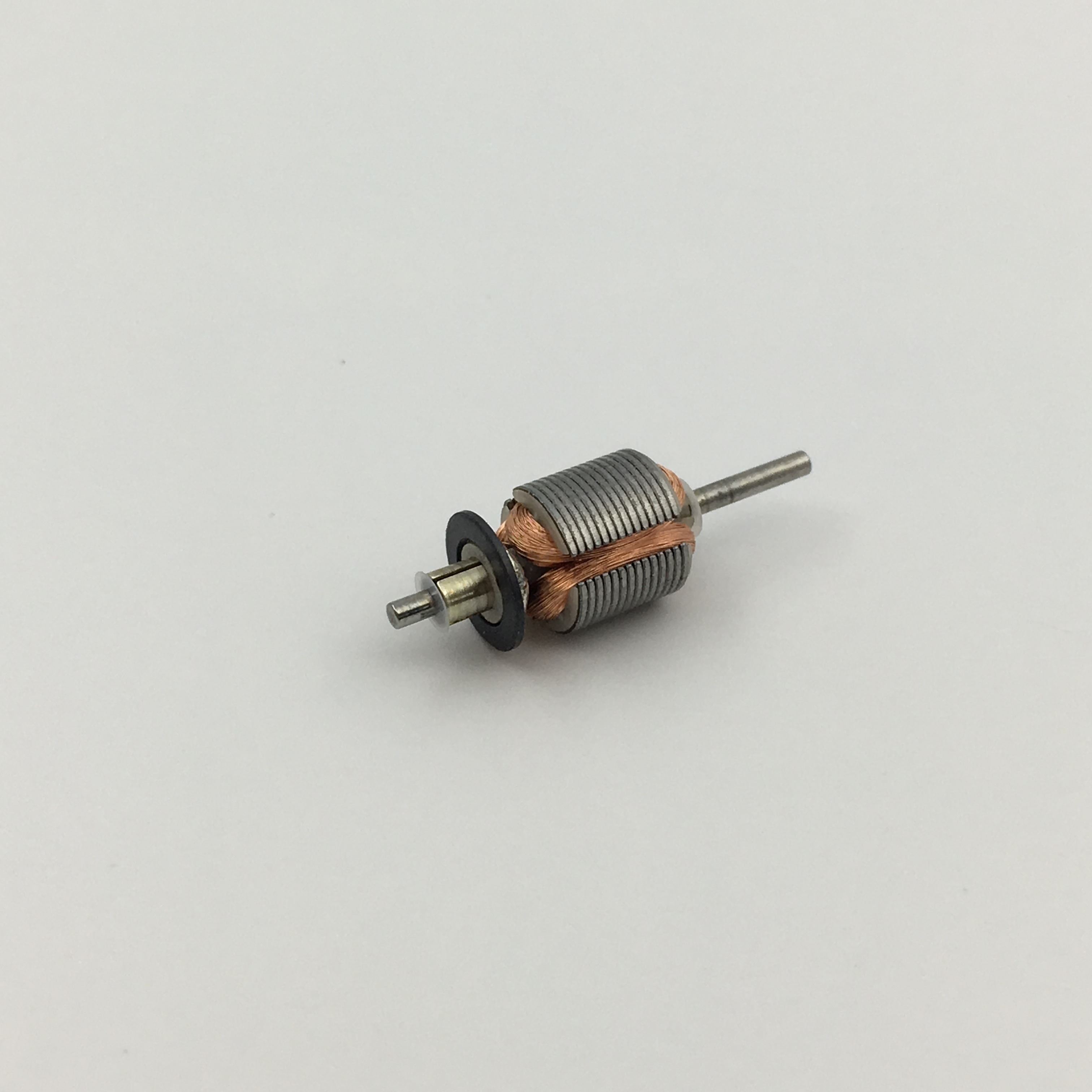
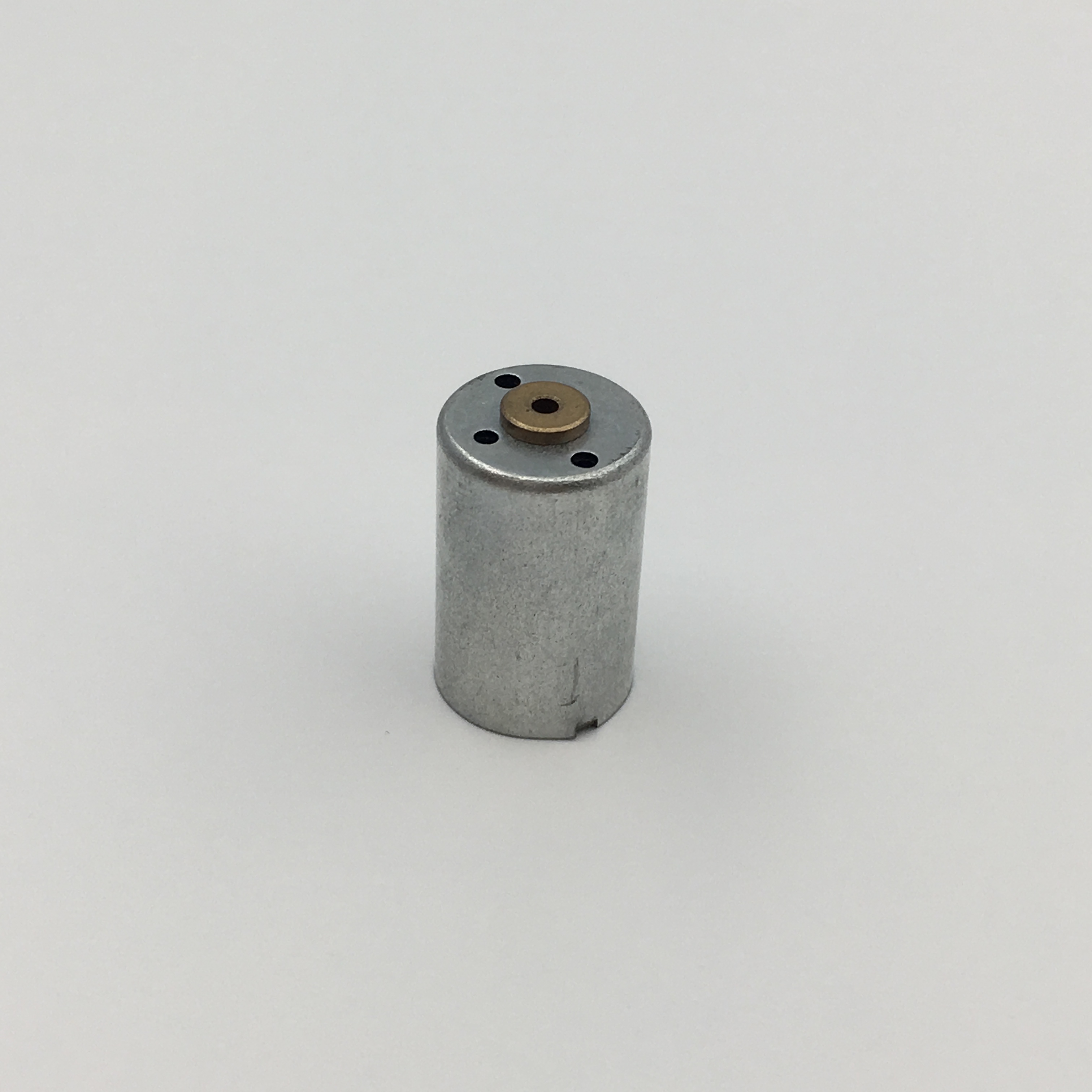



Micro motor is mainly used in: outdoor lamps, electronic toys, model aircraft, intelligent bin, breeze machine, etc



Method of use: the best stable in horizontal plane, installed on the Micro motor output shaft parts, cannot use a hammer to knock, knock prone to press into the micro motor drive, may cause damage to internal components, and cannot be used in the case of blocked.
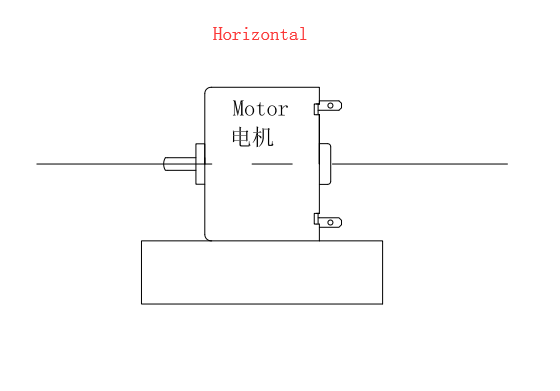
Operating temperature range:
Micro motor should be used at a temperature of -10~60℃.
The figures stated in the catalog specifications are based on use at ordinary room temperature catalog specifications re based on use at ordinary room temperature (approximately20~25℃.
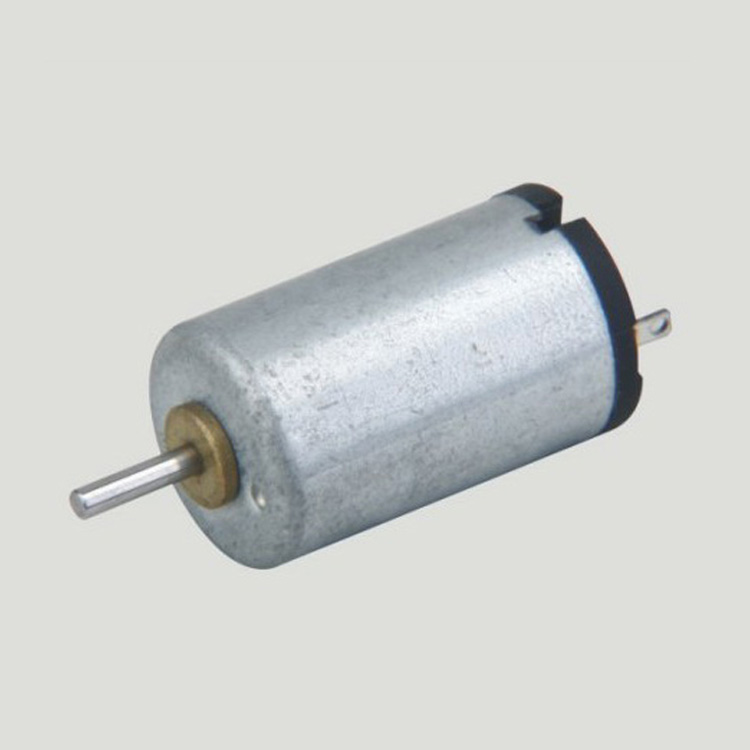
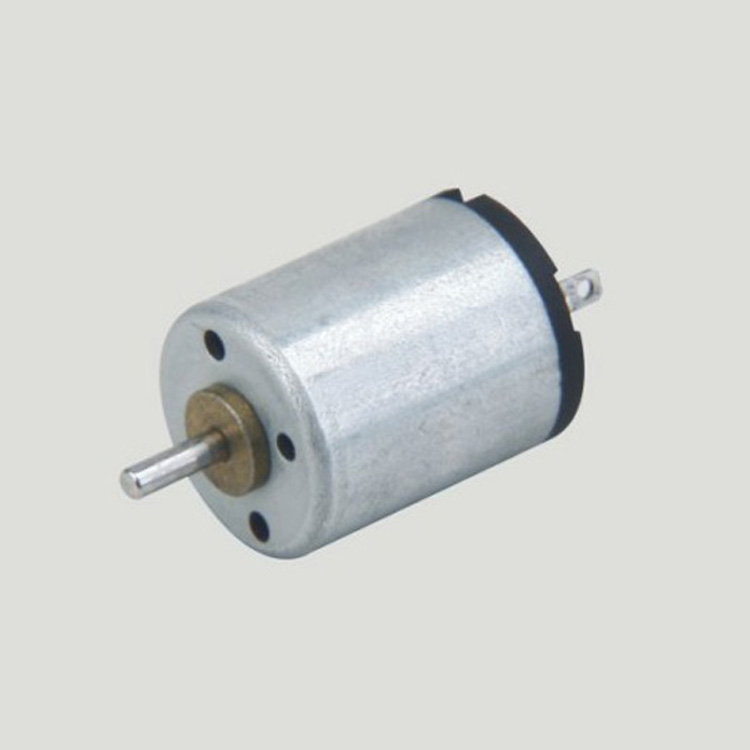


If a micro motor is used outside the prescribed temperature range,the grease on the gearhead area will become unable to function normally and the motor will become unable to start.Depending on the temperature conditions ,it may be possible to deal with them by changing the grease of the motor's parts.Please feel free to consult with us about this.
Storage temperature range:
Micro motor should be stored ta a temperature of -15~65℃.
In case of storage outside this range,the grease on the gearhead area will become unable to function normally and the motor will become unable to start.
Service life:
The longevity of micro motor is greatly affected by the load conditions , the mode of operation,the environment of use ,etc.Therefore,it is necessary to check the conditions under which the product will actually be used .The following conditions will have a negative effect on longevity.Please consult with us should any of them apply.
â—Use with a load that exceeds the rated torque
â—Frequent starting
â—Momentary reversals of turning direction
â—Impact loads
â—Long-term continuous operation
â—Forced turning using the output shaft
â—Use in which the permitted overhang load or the permitted thrust load is exceeded
â—A pulse drive ,e.g.,a short break,counter electromotive force,PWM control
â—Use of a voltage that is nonstandard as regards the rated voltage
â—Use outside the prescribed temperature or relative-humidity range,or in a special environment.
â—Please consult with us about these or any other conditions of use that may apply,so that we can be sure that you select the most appropriate model.
when it come to volume production,we're a major player as well .each month,we rurn out 600000 units,all of which are compliant with the rohs directive.Have any questions or special needed, please contact us, we have the engineer group and best sales department to service to you Looking forward to your inquiry. Welcome to our factory.

Micro Motor,Micro Dc Motor,Micro Vibration Motor,Micro Electrical Motor
Shenzhen Shunchang Motor Co., LTD. , https://www.scgearmotor.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)